Fiscally
Responsible
Outcomes and Economic
Growth
Strategy
Recover Together Strengthen. Invest. Build.
Budget 2022 is for all Manitobans. Informed by broad public consultations, it sets the path to strengthen, invest and build Manitoba around five priority areas.Emerging Ukraine Crisis and Manitoba’s Response
While Budget 2022 is looking ahead to recover together, the emerging crisis from the invasion of Ukraine will demand prompt response of the government. Manitoba is united by the outrage for the unimaginable loss and suffering being borne by the people of Ukraine forced from their homeland by the brutal war of aggression launched against Ukraine and its courageous people. Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced from their homes and millions more are seeking refuge outside of Ukraine. It is not yet known how this war will end or how many will be displaced. Manitoba government remains fully committed to welcome as many Ukrainians as possible fleeing this unprovoked and terrible war and will provide them with the full range of available provincial service supports. With the largest per capita Ukrainian population in Canada (14.5 per cent / 180,055 as of 2016), Manitoba is uniquely situated to provide assistance and welcome Ukrainian refugees into our Province.
The government’s preparations began within days of the Putin-ordered Russian invasion on February 24, 2022 for the possible arrival of thousands of Ukrainians. A dedicated and staffed Ukrainian Refugee Task Force is in place by the Manitoba Emergency Measures Organization to coordinate more detailed operational planning for the potentially large-scale arrival and settlement of Ukrainian refugees and working with the Ukrainian Canadian Congress and other Ukrainian-Canadian organizations, the settlement sector, community groups and other non-government organizations to welcome Ukrainians to Manitoba.
With the sanctions that have been imposed on Russia, we have seen significant spikes in oil prices in addition to disruptions in supply chains caused largely by the COVID-19 pandemic. These two forces have brought back the threat of inflation with the potential for higher interest rates in the near future. The Manitoba government has considered these pressures and incorporated planning and contingencies to guide Manitoba through these turbulent times.
Budget 2022 sets the path to recover together in five priority areas:
Strengthening Health Care
The highest priority is to continue strengthening health care as the government manages the surgical and diagnostic backlog, which was the outcome of the COVID-19 pandemic, and invests in the health care and long-term care systems to better respond to the needs of Manitobans.
Budget 2022 will remove barriers that delay Manitobans from getting the medical care they urgently need, address the nursing shortage, implement a renewed Seniors Care Strategy so that aging Manitobans are able to stay safe in their own homes and improve access to, and coordination of, mental health and addiction services.
The COVID-19 pandemic and its longer-term health care repercussions highlight the importance of provincial-territorial First Ministers’ unanimous request that the federal government move toward a funding partnership where the Canada Health Transfer is equal to 35 per cent of public health care spending.
Making Life More Affordable
All Manitobans are affected by the financial pressures resulting from the pandemic and the events in Ukraine. Inflation is rising. Housing prices continued to rise during the two years of the pandemic. The war in Ukraine resulted in increases oil, gas and natural gas prices. Affordability is emerging as a concern both globally and in Manitoba.
As Manitobans are facing higher household costs, the government is committed to make life more affordable to Manitobans. This is not a single strategy but an overarching theme in many of the service delivery areas across the government. This budget recognizes the affordability problems arising from inflation by making improvements to the tax system that allows Manitobans to keep more of their money.
Building Our Economy
Economic recovery and growth remains at the centre of the government’s plan for a stronger, more prosperous Manitoba. A cornerstone of the economic growth strategy is to produce employment opportunities for Manitobans, newcomers and future generations of workers.
The Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy will help accelerate the recovery, advancing Manitoba’s economy and promote positive outcomes. Promoting collaboration between advanced education institutions and employers will provide Manitobans the right skills to meet the evolving needs of the labour market. Implementing a framework to attract international investment will help businesses grow and prosper. The Manitoba government will also continue to work with the federal government on shared priorities and opportunities in transportation, strategic infrastructure, agriculture and food production.
Investing in Our Communities
The Manitoba government is committed to investing in our communities to improve the quality of life for all Manitobans. An overarching focus is working with the Indigenous peoples toward true equality and to put reconciliation commitments into action. Budget 2022 will advance shared goals and objectives through co-developed action plans, based on a foundation of dialogue and engagement with First Nations, Métis and Inuit.
The government is committed to strengthening and improving public education to better prepare students for their future. The Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education Roadmap will guide the path forward, along with a new Education Sector Council to inform provincial, local and school-level planning. Investment in 20 new schools will continue to progress. The implementation of the federal-provincial agreement on early learning and child care will reduce the cost of child care, expand spaces and enhance outcomes.
Investments in nature and heritage spaces, the arts and cultural sectors, and promoting tourism are all strengths of Manitoba that the government will build on.
Manitoba government recognizes strong and healthy communities require working with its municipal partners. Budget 2022 increases the investment into building sustainable communities program, provide infrastructure while maintaining the infrastructure support that allows municipalities retain stable funding over the long term.
Public safety plays a crucial role to improve the lives and well-being of those affected by crime and Budget 2022 makes investments to keep Manitobans safe in their communities and build public confidence in a justice system that is responsive to the needs of all Manitobans.
Protecting Our Environment
As the economy grows, it is imperative to address climate change and to protect and restore the environment. The government will undertake an energy policy framework to explore innovative technologies to reduce emissions and simulate the economy, creating a greener Manitoba for current and future generations. Budget 2022 includes funding for a wide range of green investments including renewable energy, greening transportation, funding to continue addressing rehabilitation of orphaned and abandoned mines, among others, to continue its work in protecting the natural environment and addressing climate change.
Highlights of Budget 2022 investments in the five priority areas
|
Strengthening Health Care |
|
|
Making Life More Affordable |
|
|
Building Our Economy |
|
|
Investing in Our Communities |
|
|
Protecting Our Environment |
|
Strengthening Health Care
The Manitoba government’s top priority continues to be Manitobans’ health and safety. As in Budget 2021, this year’s budget will include significant ongoing investments in the health and well-being of all Manitobans.Health Care
The COVID-19 pandemic is the greatest health care crisis in over a century. The government took many necessary measures to ensure the safety of Manitobans to provide proper care when needed. However, the pandemic also caused increased waits in the health care system for non-COVID-19 pandemic care.
Tackling the Impacts of COVID-19 in Manitoba’s Health System
The COVID-19 pandemic had significant and far-reaching collateral impacts on many aspects of the health care system.
The COVID-19 pandemic is the greatest health care crisis in over a century. The government took many necessary measures to ensure the safety of Manitobans to provide proper care when needed.
The magnitude of the COVID-19 pandemic backlog challenge includes surgical and diagnostic waits, cancer screening and diagnoses, and waits and increasing demands for other important services to Manitobans. For example, the Canadian Partnership Against Cancer and Canadian Association of Provincial Cancer Agencies (CAPCA) publicly reported in June 2021 that various jurisdictions across the country are seeing a 20 per cent reduction in cancer diagnoses. This means that there is likely to be later-stage disease diagnoses and resulting pent-up demand for timely services, as the province emerges from the pandemic.
The pandemic has also placed significant pressure on the health care workforce, in particular those on the front lines. A March 2021 national health human resources report identified that health care workers are dealing with a so-called syndemic – a term for multiple epidemics in various areas occurring at the same time. Thus, it is anticipated that there will be many long-term impacts on individual health care workers that will last well beyond when the pandemic is deemed ‘over’ and addressing these impacts will require support, recovery strategies and interventions.
Responding to the challenge
The Manitoba government has already recognized that significant financial resources will be needed to address the multiple challenges. Budget 2021 contained a total of $50 million to support the backlogs in activity in that fiscal year alone.
Budget 2022 continues to address the pandemic backlog by providing a total of $110 million to aid in the recovery from COVID-19 related to surgical and diagnostic backlogs.
Work is underway but is further complicated by the global health human resource challenges. To this end, the need for increases in health services activity, coupled with increased global demand for skilled health human resources who are in short supply, requires innovative solutions. In addition, the evidence is pointing to an activity level that is greater than simply a restoration to the pre-COVID-19 status quo state. To respond to this challenge, a multi-faceted approach will draw on the expertise and engagement of the entire provincial health system.
Addressing Diagnostic and Surgical Backlogs
Manitoba government has created a Diagnostic and Surgical Backlog Task Force to work across a number of streams to address the diagnostic and surgical backlog challenges. The five-point plan includes the following actions:
1. improve the capacity of the existing provincial health system to deliver activity
2. increase provincial capacity through more intensive health care purchasing efforts
3. engage the front line in finding solutions
4. apply innovations developed locally and globally
5. engage citizens and community in identifying challenges and finding solutions
The plan will use improvements in the capacity of the existing provincial system to deliver more activity, such as streamlining processes and patient journeys to help address the surgical and diagnostic wait-list backlog. The government is also implementing wait-list management and prioritization strategies to prevent worsening of the backlog.
The Manitoba government has established this task force to address the diagnostic and surgical backlogs as the top priority for the health system coming out of the pandemic. The Diagnostic and Surgical Recovery Task Force will also address wait-lists for diagnostic and surgical procedures affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. This will include identifying the priority needs of patients and implementing local, and out-of-province services as a temporary initiative, to offer the safest and most timely health care solutions available. The task force includes individuals with significant expertise related to surgical and diagnostic services, analysis and evaluation, and project management. A steering committee has also been established to set the direction of the task force and access the expertise of Manitoba’s health care system. The steering committee members include physicians, nurses and patient and citizen representatives. Initiatives already announced by the task force include an agreement with Maples/Clearpoint in Winnipeg to address gynecological surgery and an agreement with Sanford to perform spine surgery. Budget 2022 contains these and more initiatives recommended by the Task Force, which will be occurring over the spring.
Increasing provincial capacity, through more intensive health care purchasing efforts called Request for Services Agreement or RFSA process, began in the summer of 2020. RFSA allowed Manitoba to perform 5,500 procedures at locations like CancerCare Manitoba, Western Surgery Centre, Pan Am Clinic and Vision Group. These additional procedures included over 3,000 cataracts, 1,800 echocardiograms, over 250 foot and hand procedures, and several other types of surgical procedures. In 2021/22, the RFSA process has brought more than 9,000 additional procedures to Manitobans that were waiting for care. These included more than 4,800 cataracts, over 600 foot and hand procedures, and over 600 pediatric dental surgeries.
In 2022/23, Manitoba Health is setting aside $110 million to address the surgical and diagnostic backlog. A Request for Services process that will allow existing Manitoba providers and potential new entrants to undertake additional procedures. The government will also explore additional opportunities with clinical providers and organizations throughout Manitoba so this additional capacity can be harnessed to deal with the backlog in a more timely way. Work is also underway to collaborate with out-of-province providers for some needs that are emerging due to waitlists that cannot be addressed in a timely manner. While the government’s goal is always to provide care as close to home as possible, it will continue to examine safe and innovative ways to get faster care to Manitobans.
Manitoba is addressing the international health human resource challenges that contribute to waits for care, by introducing innovative practices:
Maintaining virtual services that emerged in the pandemic for non-COVID-19 care as the province emerges from the pandemic. For example, the Virtual COVID-19 Outpatient Program (VCOP) provides home care to patients with COVID-19 to support those who may require home oxygen and/or support during their recovery. VCOP is available in Winnipeg, Brandon, Portage la Prairie, Steinbach, Winkler/Morden and Selkirk. To date, the program has cared for 504 patients and approximately 3,641 in-patient days in hospital have been saved, giving patients a safe alternative that allows them to be cared for remotely at home while freeing up hospital and staffing resources to care for patients that must remain in hospital for care.
Another excellent innovation is in echocardiography. Wait times for elective echocardiograms exceeded national targets. After the COVID-19 wave in June 2020, there were 7,279 echocardiograms in the queue and wait times were 45.3 weeks. Since last spring (July 2020 to June 2021) Shared Health Diagnostics completed 28,958 echocardiograms and the RFSA (other echo providers) performed another 2,690 echocardiograms. By the end of June 2021, wait times had been reduced by more than 38 weeks to seven weeks and the waitlist had dropped by 68 per cent. This was accomplished in part, by hiring the Red River College Polytec graduating class of echocardiography students.
These are examples of the great work that is already underway to support the diagnostic and surgical recovery efforts in Manitoba.
The Manitoba government is engaging communities in this work through a commitment to regular, public reporting of progress and through the composition of the Task Force Steering Committee. This committee and the project team is identifying the most impactful strategies to make further strides in providing Manitobans with access to the safest and most timely care possible. The task force includes front-line health care professionals to help ensure the government’s plans make sense on the front lines where care is provided. Citizens and patients have been included on the Task Force Steering Committee so the voice of patients and families are involved in the solutions being developed. It is also why the government commits to transparent, regular reporting to Manitobans on progress throughout 2022/23.
Clinical and Preventive Services Plan
As first announced in Budget 2021, Manitoba is making an historic $812 million capital investment in building, expanding and renovating health care facilities across the province in support of Manitoba’s Clinical and Preventive Services Plan. The plan, led by clinicians, improves access to care for all Manitobans and identifies planned investments in health infrastructure as being pivotal to efforts to support better care sooner and as close to home as possible.
Manitoba’s Clinical and Preventive Services Plan will guide improvements to access, quality and patient outcomes for all Manitobans. Developed with the extensive input of health care professionals, communities, and members of the public, the plan represents the first time that clinical providers have contributed to a provincial plan that will meet the unique needs of Manitoba communities. Improvements or new hospital developments in Manitoba include the following sites:
- $127 million for a new Hospital in Neepawa
- $5 million for new endoscopy, chemo therapy spaces at Dauphin Regional Health Centre
- $31.6 million expansion of the Selkirk Regional Health Centre
- $64.4 million expansion at the Boundary Trails Health Centre
- $32 million expansion of the Bethesda Regional Health Centre
- $283 million for a new hospital in Portage la Prairie
- $70 million to enhance health services in Brandon including addition and renovations at the Brandon Regional Health Centre and expansion and renovation of the Western Manitoba Cancer Centre
- $10.8 million for renovations to Ashern’s Lakeshore General Hospital
- $115 million in northern Manitoba
All of these initiatives are currently in implementation, including design planning.
COVID-19 Pandemic Response
Manitoba will continue its pandemic response until the pandemic is over. While the province is moving through the end of the omicron wave, the situation and COVID-19 variants are constantly evolving. As a result, the end date of the pandemic is unknown with certainty at this time. Since the health sector is a lagging indicator, it must stay in a state of readiness to be ready to deal with subsequent surges or remnants of the pandemic. The government must also plan for an orderly transition from an emergency response back to regular operations and intentionally plan for the recovery of the health system including staff resiliency and retention efforts.
To continue the ability to respond to the pandemic, Budget 2022 will once again include funding that can be used for a variety of response measures.
Manitoba will retain the positive learnings from the pandemic in virtual services and utilize them after the pandemic. Virtual physician visits have been embraced as many people have found virtual physician visits for certain medical consultations to be convenient. It has also avoided the burden of unnecessary travel.
Manitobans were also given broader access to lab results and immunization records during the pandemic. These advancements will be continued after the pandemic.
Health Transformation
The changes that Health Transformation has brought about in the health care system can help to propel Manitoba forward. The health care system in Manitoba is poised to improve its performance as a result of changes in recent years. These changes have established the foundation to work better as one provincial system. Roles of each organization are clearer and each organization has a key role to play in excellent service delivery.
For example, recent efforts by Shared Health and the five Regional Health Authorities and Selkirk Mental Health Centre to work more closely as a unified provincial system have been very successful in addressing the backlog of patients that were in hospitals awaiting placement in personal care homes.
The changes that Health Transformation has brought about in the health care system can help to propel Manitoba forward. The health care system in Manitoba is poised to improve its performance as a result of changes in recent years.
Although delayed by COVID-19, Wave II of the Health System Transformation continues to implement Manitoba’s Clinical and Preventive Services Plan (PCPSP). The PCPSP is focused on sustaining health services into the future so that care is optimized, guiding investments in rural and northern health care, digital health supports and infrastructure investment in projects and program delivery.
Other work that will arise from the implementation of PCPSP will result in improved capacity of the system through additional procedures outside of Winnipeg, improvements in home care to avoid hospitalizations, greater use of e-consults, virtual visits and other tools that modernize the care provided in Manitoba.
Highlights of ongoing investments include:
- Continued investments in renal replacement therapy for both in-centre dialysis located at health centres across Manitoba as well as home hemodialysis programs. An additional investment of $1.8 million will result in an additional 937-person patient capacity across these renal programs provincially. A total of 22 station dialysis units, supporting up to 132 patients, opened within the Diagnostic Centre of Excellence (DCE) capital building project at the Health Sciences Centre in Winnipeg on March 1, 2021. The funding will further expand in-centre capacity at Brandon to 12 patients and 24 patients in Portage la Prairie, and provide for a new renal site in Steinbach which will accommodate 24 patients. Since 2015/16, $34.1 million in total funding has been approved to expand dialysis capacity.
- To date, the Manitoba government has completed or is in active design/construction for 754 beds and has approved funding for the construction of a total of 1,099 new and replacement PCH beds.
- An increase of $7.6 million is being provided for Emergency Response Services including for the hiring of 35 additional primary care paramedics (PCPs) as part of the government’s commitment to hire an additional 80 paramedics to achieve customer service standard of 24-7 access to care within 30 minutes for 90 per cent of Manitobans, 90 per cent of the time by 2023.
- $7.2 million more is being provided to support two Home and Community Care Modernization pilot projects, the Priority Home and Client Directed Funding Pilot and Supportive Housing Pilot, to provide more safe spaces for seniors and to improve home and community based care.
- An increase of $640,000 is being provided for the continuation of the Forensic Nurse Examiner Program in Brandon, Thompson and The Pas. The program provides for specially trained nurses who provide treatment to victims of sexual assault including forensic evidence collection. This expansion addresses the inequality of access to services for patients in rural and remote areas.
- An increase of $450,000 is being provided to support the distribution of additional naloxone kits to people with problematic substance use.
- The Manitoba government is also providing funding to continue to support the implementation of Young Adult Insulin Pump Program including to extend coverage of insulin pumps to individuals aged 18 to 25.
Federal Funding Partner in Health care
Historically, the federal government has played an important role in helping support provincial and territorial health care services. Canada responded to provinces’ and territories’ needs during the pandemic to address immediate health system pressures.
However, since the mid-1990s, the federal government has taken several measures to reduce its overall contribution flowing through the major federal transfers. This has resulted in systemic pressures across provincial and territorial health care systems to meet the diverse and growing needs of Canadians.
Sustaining the level of care to respond to Manitoban’s greatest health care needs going forward requires an increase in share of the Canada Health Transfer (CHT) of provincial and territorial health spending to 35 per cent.
Manitoba is currently working with all of the other provinces and territories, through the Council of the Federation, to negotiate enhancements to the CHT that will represent a renewed and reinvigorated health care funding partnership with the federal government.
When the major federal transfers are adequate, responsive and sustainable, they help foster a stronger and more resilient Canadian economic and social union.
Refer to Federal-Provincial Fiscal Partnership for more information, page 133.
Seniors and Long-term Care
The pandemic exposed gaps in Manitoba’s long-term care system here and across Canada, and drew the focus to seniors who were not receiving the dignified care they deserve.
These gaps are reflected in an external government commissioned review, led by Dr. Lynn Stevenson, in regards to the serious outbreak of COVID-19 that occurred at the Maples Long Term Care Home between October 20, 2020, and January 12, 2021, where 73 staff and 157 residents tested positive, and 54 residents died.
Stevenson identified gaps at the facility level as well as system level, reviewing funding for personal care homes to ensure that staffing levels and services provided are appropriate to the complexity of current and future residents, and reviewing and streamlining the licensing standards for PCHs to ensure currency and applicability to the changing needs of residents.
The Final Report of the Provincial Implementation Plan for the Stevenson Review, released April 2022, shows the significant progress that has been made in implementing the 17 recommendations of the Stevenson Review.
The Final Report of the Provincial Implementation Plan for the Stevenson Review, released April 2022, shows the significant progress that has been made in implementing the 17 recommendations of the Stevenson Review. Approximately $43 million was spent in 2021/22 to support the seniors in personal care homes as part of the COVID-19 response with a portion of this funding in direct response to the Stevenson Review recommendations.
While implementation is well underway, ongoing oversight is needed to assure Manitobans that changes to the personal care homes are fully implemented and sustained over the coming years. To that end, the Manitoba government has established a new minister and Department of Seniors and Long-Term Care that will provide stewardship to the implementation of the changes.
The minister of seniors and long-term care is also mandated to consult with Manitobans and stakeholders to modify, enhance and implement a renewed Seniors Strategy so that aging Manitobans are able to stay safe in their own homes and communities as long as they choose.
Manitoba has a growing seniors population, and their preferences and best practices in supporting older Manitobans to stay safe in their homes and communities are evolving.
Over the next 20 years, Canada’s older adult population is expected to grow by 68 per cent, with the population in Manitoba expected to increase two times its current size (Canadian Institute for Health Information, 2017). Today, 23,000 Manitobans have Alzheimer’s disease or dementia. Today, older Canadians living in rural areas are 50 per cent more likely than urban dwellers to be admitted to personal care homes when they could have been cared for at home.
Mental Health
Over the last several years, there has been significant progress made in reducing the stigma associated with mental health and substance use issues, leading more Manitobans to seek help when needed. However, many measures of Manitobans’ mental health and well-being have been poor when compared nationally. This has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which continues to have a significant impact on mental health and wellness.
Recognizing this, the Department of Mental Health and Community Wellness has developed a whole of government plan to improve the system and increase access to mental health and community wellness services for Manitobans. In 2021, the department led province-wide consultations, speaking to thousands of Manitobans, service providers and experts about opportunities to improve mental health, substance use, recovery and wellness programs and services in the province. Through the consultations, the department heard that the pandemic has placed added pressure on an already stretched mental health and addictions system. The pressures of increased demand, and ensuring physical distancing have impacted program and service capacity and increased wait lists for many programs.
The consultations informed the development of the department’s five-year roadmap, A Path to Mental Health and Community Wellness: A Roadmap for Manitoba. The roadmap’s vision is that Manitobans experience optimal physical, mental, emotional, cultural and spiritual well-being across their lifespan.
1. Equitable Access and Coordination
2. Mental Well-Being and Chronic Disease Prevention
3. Governance and Accountability
4. Quality and Innovation
5. Indigenous Partnership and Wellness
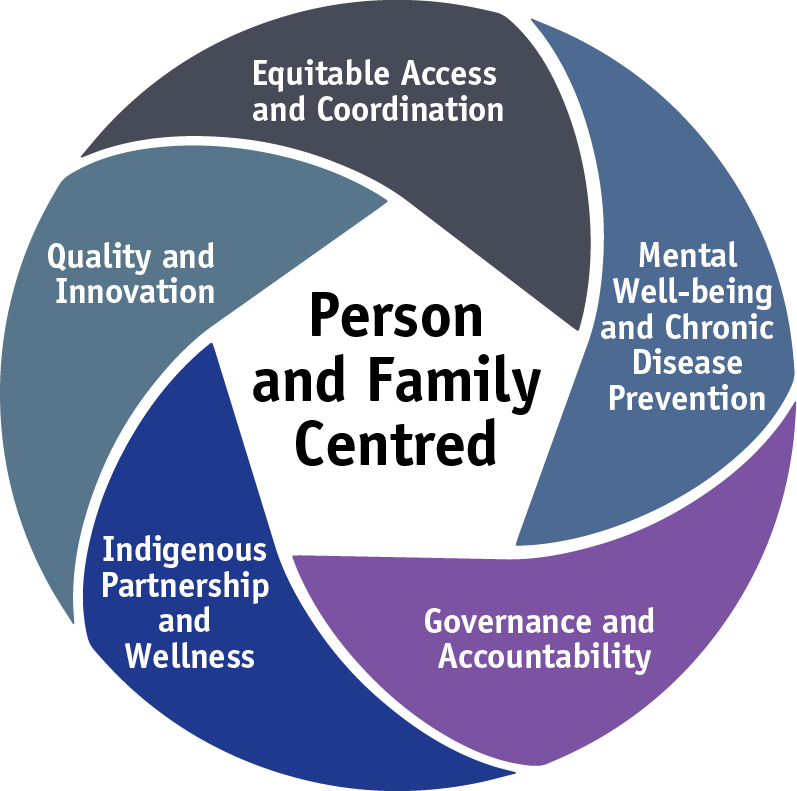
Through implementation of the roadmap, investments will be made in core services and programs for Manitobans, to make services more available and easier to navigate. The department will continue to work using a whole-of-government approach to guide the roadmap’s governance, decision-making and actions. Investments will be informed by needs-based planning that will be conducted across the province, to help ensure that services are available across different levels of need.
Budget 2022 will make the following investments to address system pressures, increase capacity of front-line services and ensure the continuity of successful mental health and addictions initiatives:
Pandemic Recovery
- mental health promotion and universal supports
- children and youth with complex, multi-system needs
- mental health, addictions and trauma support
Initiatives supported through this funding will also include a range of Indigenous-led programs and supports, peer support programs, addiction services and mental health supports for children and youth.
Refer to the following link to the department of mental health and community wellness website to access the A Path to Mental Health and Community Wellness: A Roadmap for Manitoba: www.manitoba.ca/mh/ .
Smoking Cessation Social Impact Bond
The Manitoba government has launched its first health related Social Impact Bond, entitled “Quit Smoking with your Manitoba Pharmacist” to strengthen access to smoking cessation supports and improve the health and wellbeing of our communities. “Quit Smoking with your Manitoba Pharmacist” is a pharmacist led intervention which delivers nicotine replacement therapy and counselling to individuals who wish to quit smoking. This program is accessible to anyone over 18 years of age interested in quitting smoking by speaking with their local participating pharmacy.
Making Life More Affordable
Affordability and Taxes
All Manitobans are affected by the financial pressures resulting from the pandemic, and the events in Ukraine.All Manitobans are affected by the financial pressures resulting from the pandemic, and the events in Ukraine.
Inflation is rising. Housing prices have continued to rise despite the pandemic. There have been recent increases in oil, natural gas and gasoline prices caused by the war in Ukraine. Supply chains have been strained. These have created additional pressures on affordability, not only in Manitoba, but globally.
The government recognizes these challenges, and is committed to investing in families, education, and economic development to keep Manitoba as an affordable place to live.
Quality of life and value for money are priorities for the Manitoba government and includes letting Manitobans keep more of their money.
The COVID-19 pandemic has challenged governments and families worldwide in many ways, but here in Manitoba it has highlighted more than ever the importance of affordability when faced with economic or financial adversity, and a need for a competitive tax regime to limit the burden on businesses and families during trying times.
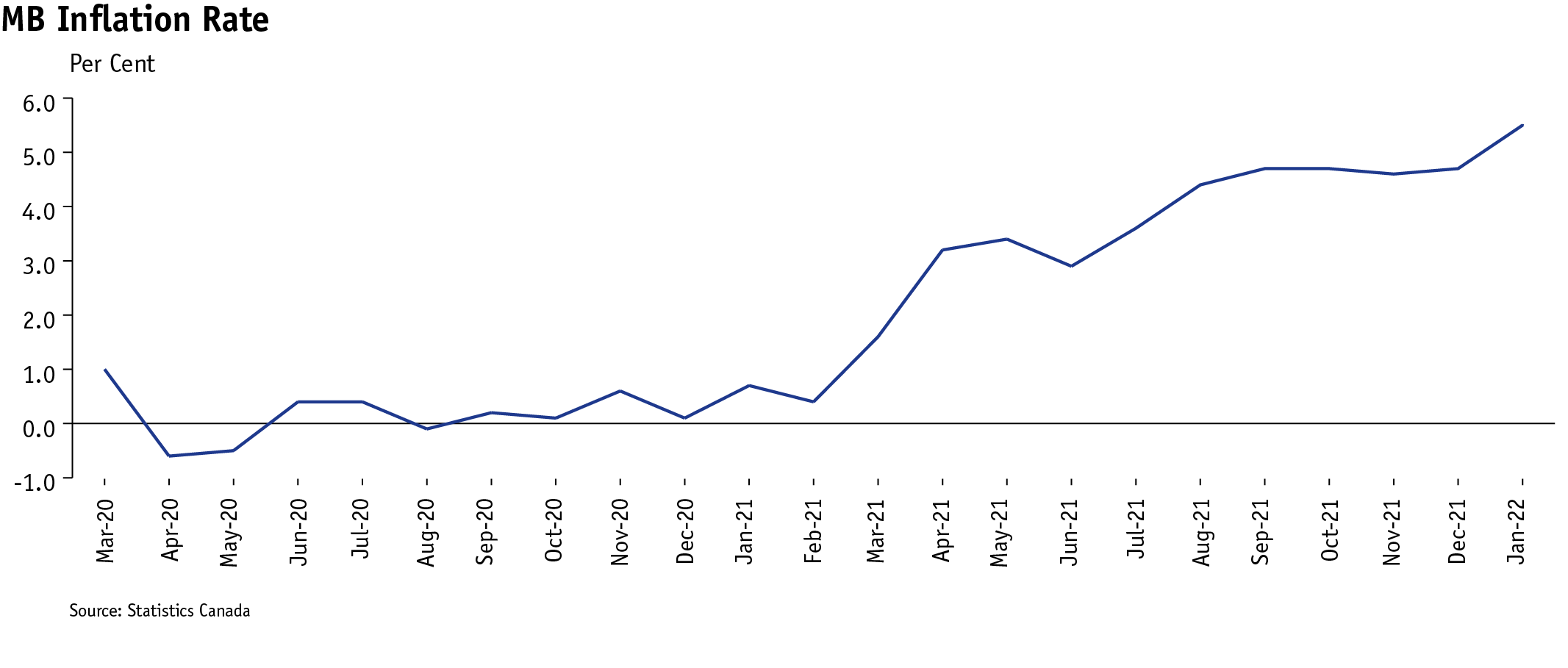
Manitobans are facing higher household costs as inflation rates increase, as reported by the Statistics Canada Consumer Price Index. Inflation in Manitoba is driven by higher utility costs, gasoline prices and food prices that families and individuals experience in their daily lives.
According to the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) Rental Market Report, the Winnipeg vacancy rate is a healthy five per cent due to 2,915 units being added in 2021, the largest increase since 1990. CMHC has also previously noted the vacancy rate for lower income renters is much tighter and over 90 per cent of this cohort resides in bachelor and one-bedroom suites, making it difficult for larger households to access affordable rents.
According to the Manitoba Real Estate Association, 2021 housing sales outpaced 2020 and drove housing sale prices up considerably, to $338,772 in January 2022 from $304,759 in January 2021. The Bank of Canada indicated in 2021 that interest rates could increase in 2022 if high inflation rates persist. On March 2, 2022, the Bank increased its policy rate from 0.25 per cent to 0.50 per cent. A one-percentage point increase in interest rates on the first-year mortgage on an average house is almost $2,500.
These trends are reflected in the perspective of families and households on their financial futures. According to the January 2022 MNP Consumer Debt Index for Manitoba (and Saskatchewan):
- Nearly half of the residents are not confident they can cover their living expenses this year.
- Four in 10 are concerned about their current level of debt.
- Less than a quarter are confident in their ability to cope with unexpected events without increasing their debt.
- Two in 10 believe their current debt situation is worse than it was a year ago.
- Four in 10 say they are finding it even harder to pay down debt.
Lowering Taxes
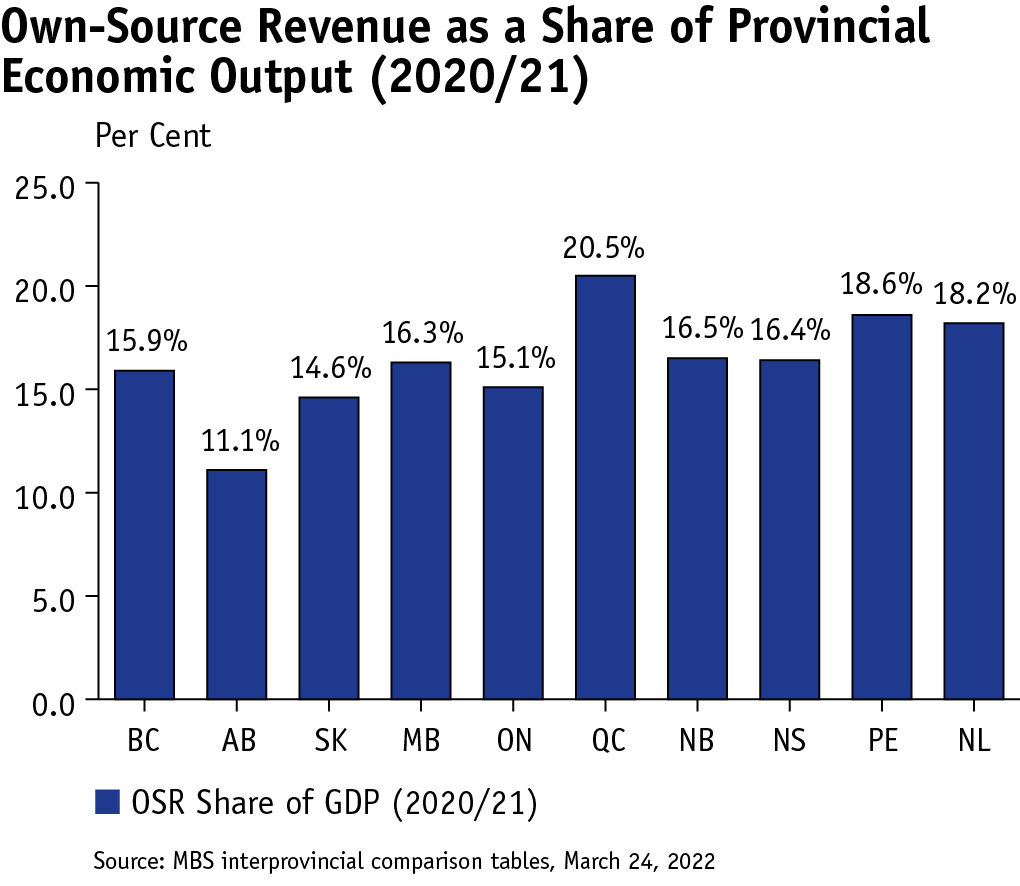
Manitoba’s overall tax environment is less competitive compared to provinces west of Quebec. Manitoba’s own-source revenue, which includes tax and other revenue and excludes federal transfers to Manitoba, as a share of the provincial economy is higher than that of provinces west of Quebec.
In an effort to improve competitiveness, the Manitoba government, since first being elected in 2016, has provided $886 million in tax savings, including $607 million to families and individuals and $279 million to businesses.
This includes the reduction in the sales tax rate to seven per cent from eight per cent, now the second-lowest provincial rate in Canada. The government continues the phasing out of education property taxes that began in 2021.
Other important savings of nearly $90 million include eliminating sales tax on residential and non-residential property insurance premiums and on the preparation of wills, the preparation of personal income tax returns and on personal services.
Relief has also come in the form of fee reductions. Specifically, probate fees were eliminated and non-commercial vehicle registration fees were reduced by 20 per cent.
Indexing the basic personal amount and the personal income tax brackets protects Manitoba taxpayers from the impacts of inflation. Since 2017, these tax variables have been tied to the Manitoba Consumer Price Index, which serves as an index factor. Indexing has provided annual tax relief of up to $39 million depending on the index factor for the previous year and, because of its compounding benefits, is worth nearly $162 million in 2022.
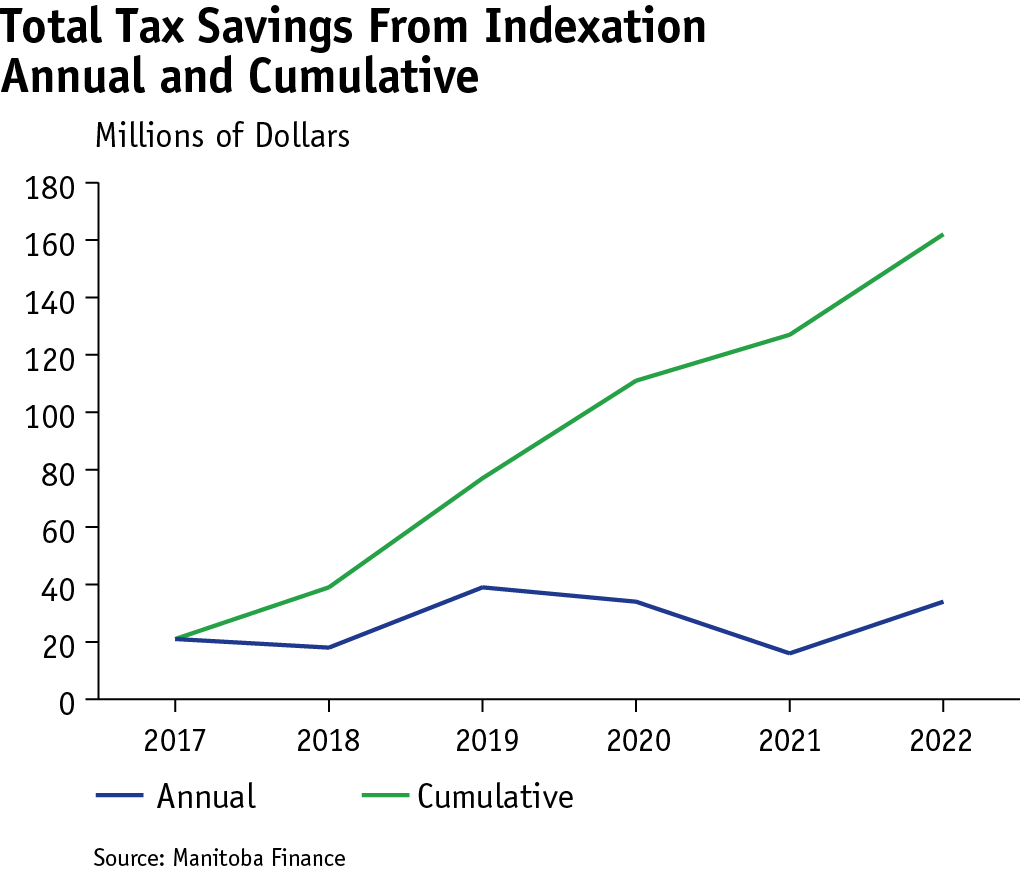
Because of legislated indexing, the cumulative tax savings by 2022 for an individual at the highest bracket is $523.
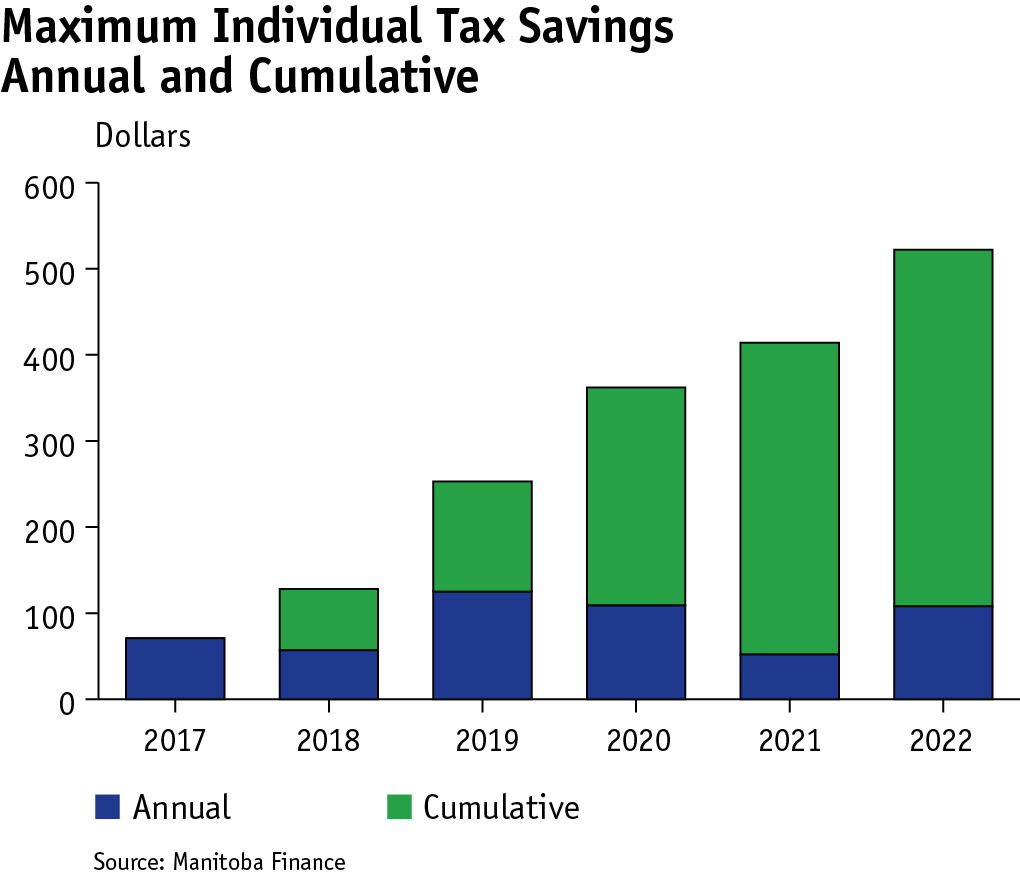
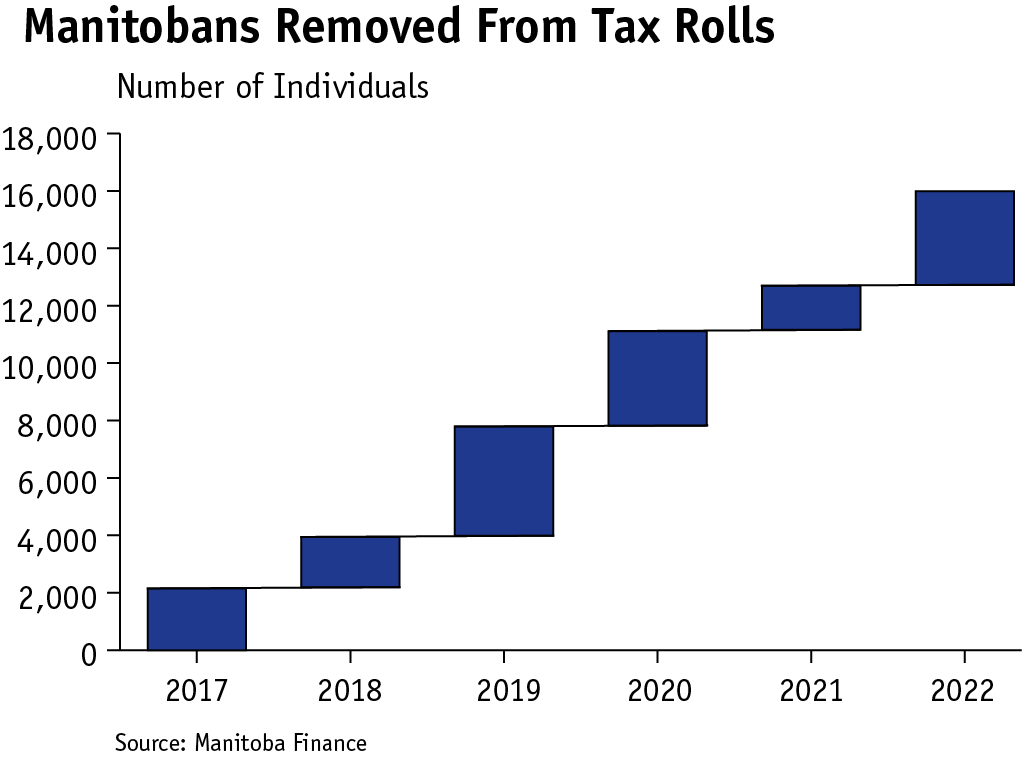
Indexing also removes Manitobans from the income tax rolls. By 2022, 15,780 Manitobans will no longer pay Manitoba income tax due to increase in the basic personal amount.
Education Property Tax Rebate
Budget 2021 commenced the 10-year phase-out and elimination of education property taxes in Manitoba with the introduction of the Education Property Tax Rebate in 2021, which provided 25 per cent school tax rebate cheques to residential and farm property owners and 10 per cent school tax rebate cheques to other property owners.
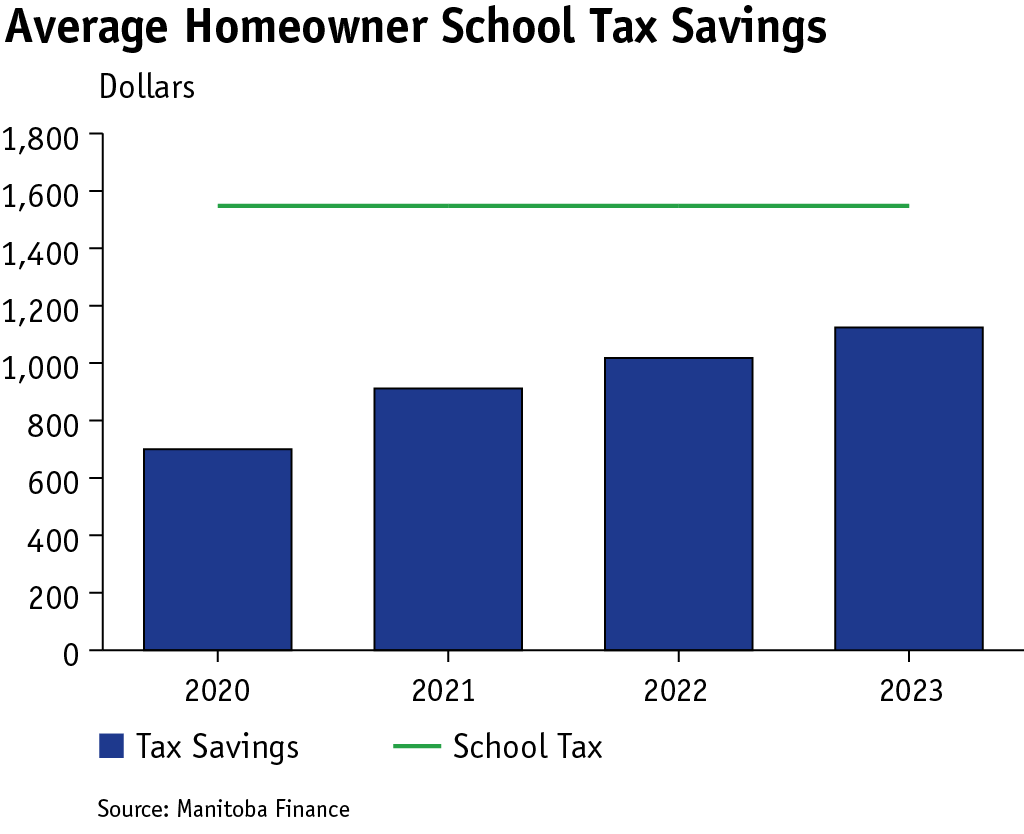
Total savings from the rebate is equal to $246.5 million in 2021, $350 million in 2022 and $453.2 million in 2023; a combined value of over $1 billion for the three years.
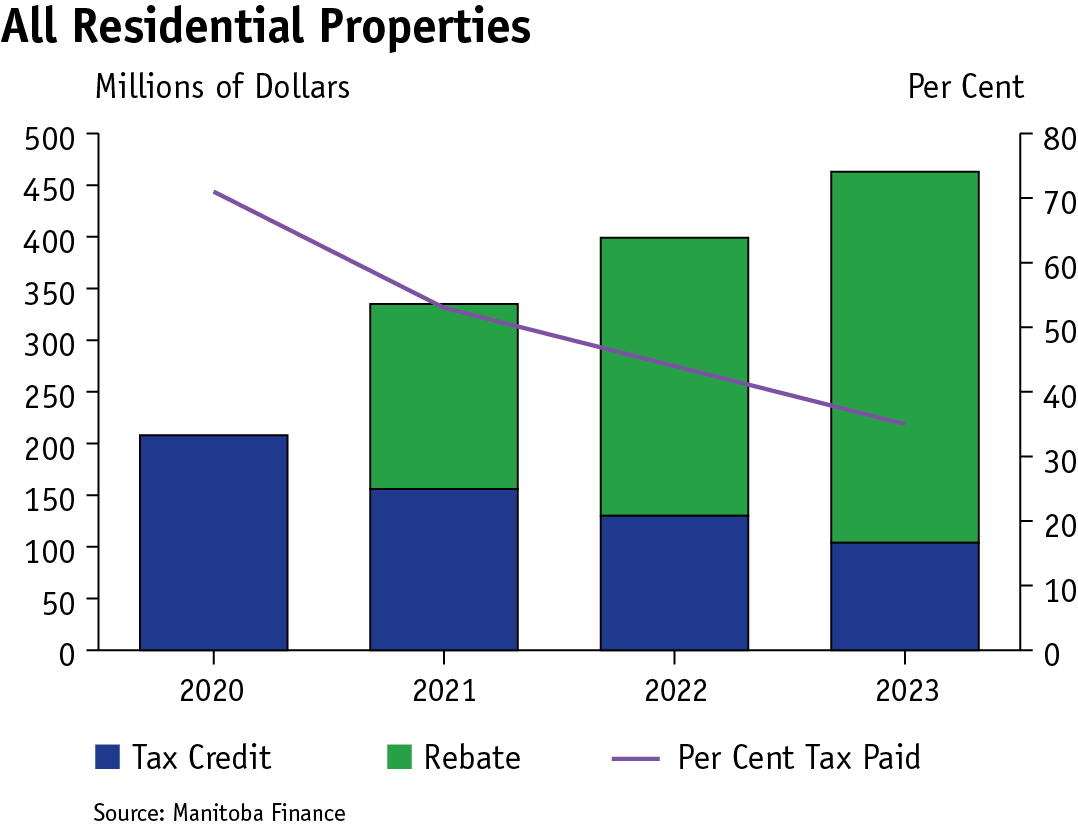
By 2023, nearly half, 48 per cent, of total school taxes paid by all property owners will be offset by the Farmland School Tax Rebate, Education Property Tax Credits and the Education Property Tax Rebate.
For residential properties, net school tax (per cent tax paid) will decrease to 35 per cent in 2023 from 71 per cent before the introduction of the Education Property Tax Rebate as the value of tax credit and rebate savings increase to $463 million in 2023 from $208 million in 2020.
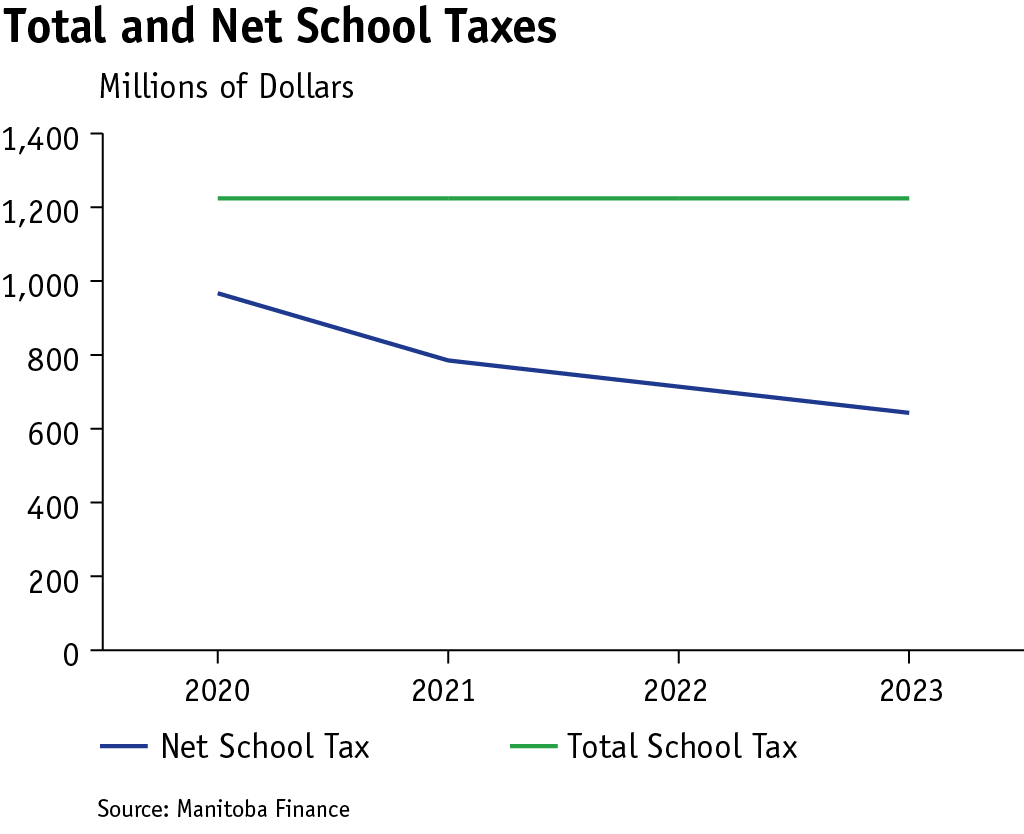
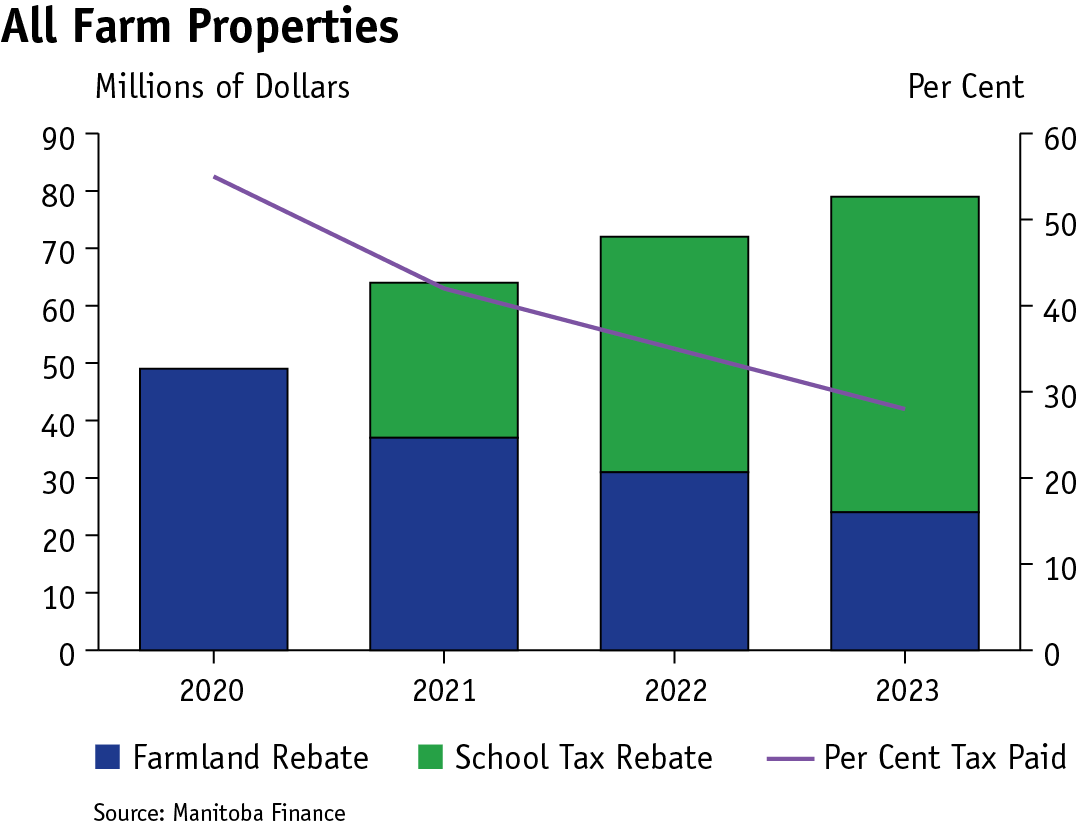
On farm properties, the savings are more pronounced. The per cent of net school tax (per cent tax paid) will decrease to 28 per cent in 2023 from 55 per cent in 2020 as the value of rebates savings increase to $79 million in 2023 from $49 million in 2020.
Renters Tax Credit
Approximately 40 per cent of Manitoba households reside in residential tenancies and pay monthly rent. Since the inception of the Education Property Tax Credit, homeowners and residential renters have qualified for the same credit. For homeowners, eligibility is based on education property taxes. For renters, the credit has been the lesser of 20 per cent of total rent paid for the year or the maximum Education Property Tax Credit.
Three significant enhancements are also made under the Renters Credit. First, the annual amount will be fixed at $525, the same amount as in 2021 under the other tax credit program. Secondly, those enrolled in Rent Assist and not on Employment and Income Assistance will now qualify fully for the Renters Credit, benefiting up to 11,000 households. Finally, Manitobans in social housing, who pay rent geared to income and did not qualify for the renters Education Property Tax Credit, will now qualify for the Renters Credit. This will benefit up to 34,000 households in social housing and means that up to 45,000 households with lower incomes will qualify for up to $24 million in new Renters Credits starting in 2022.
For a household paying the average $1,000 per month in rent, the Renters Tax Credit is equal to over half of one month’s rent.
|
Tax Credits for Renters |
|||
|
Non-EIA Rent Assist |
Social Housing |
Other Renters |
|
|
2021 (Education Property Tax Credit) |
Yes
|
||
|
2022 (Renters Tax Credit) |
Yes
|
Yes
|
Yes
|
Health and Post-Secondary Education Tax levy
Creating jobs is both a necessity to generating economic growth and a consequence of growth. It has long been said that small businesses are the mainstay of Manitoba’s economy. Whether it is the self-employed local grocer, the family farmer, the local doctor, accountant or lawyer, all contribute broadly to the provincial economy.
In 2021 and 2022, Manitoba reduced the impact of the Health and Post-Secondary Education Tax Levy by increasing the exemption level and reduction level at which a lower tax rate is paid.
In 2021, the exemption level was increased to $1.5 million from $1.25 million and the payroll threshold at which a lower tax is paid increased to $3 million from $2.5 million, benefiting 1,000 employers including exempting 220 employers.
In 2022, the exemption level was increased to $1.75 million and the payroll threshold to $3.5 million, benefiting 1,100 employers including exempting 240 employers.
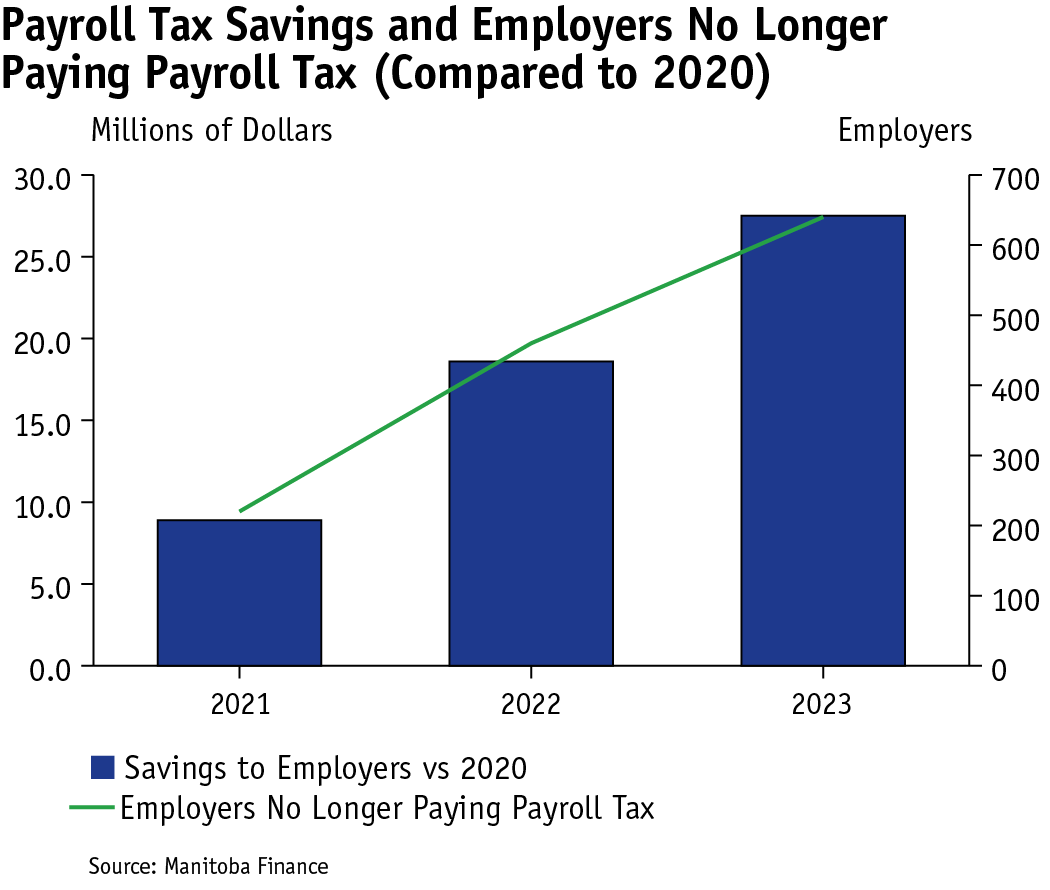
In total, the changes since 2020 are saving employers over $27 million annually, and 640 employers will no longer face payroll tax liabilities and are allowed to grow and continue to not pay the tax.
Supporting the Peat Harvesting Industry
Marked fuel can be currently purchased tax exempt when used in off-road machinery and equipment utilized by the farming, mining, commercial logging, commercial fishing and trapping industries. Extending this exemption to peat harvesting equipment supports this industry in Manitoba and is consistent with tax treatment in the majority of Canadian jurisdictions.
Vehicle Registration Fees
This follows reductions in both 2020 and 2021 and completes the government’s commitment to roll back the increase to vehicle registration fees by 30 per cent by 2023. Promise made, promise kept.
The 30 per cent total reduction results in savings of $45 million a year to Manitobans. The vehicle registration fee reduction applies to most non-commercial vehicles, such as passenger vehicles, trucks, trailers, and motorcycles or mopeds.
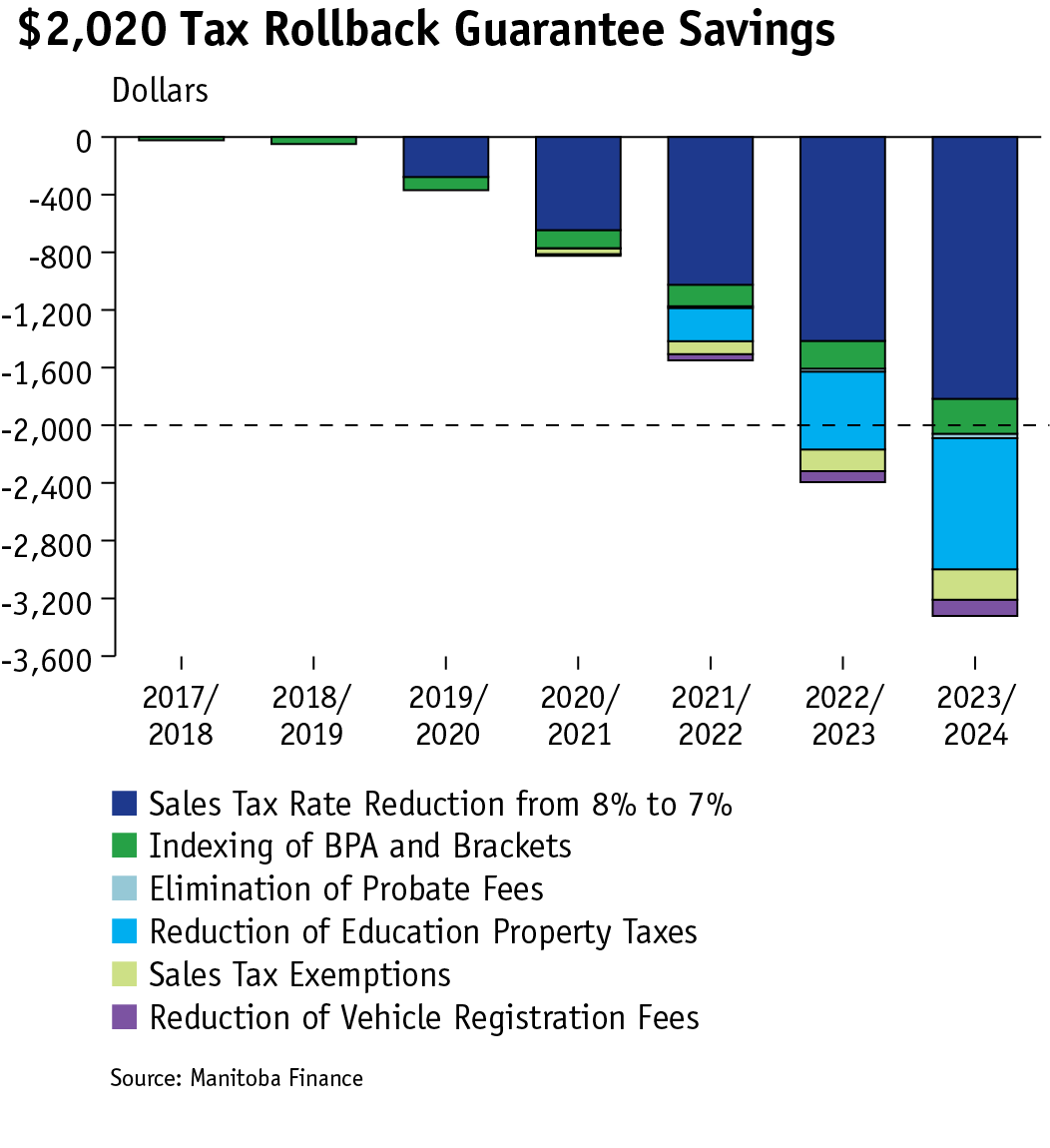
Meeting our $2,020 Tax Rollback Guarantee
During the last election we promised to return $2,020 to Manitoban households over the next four years. In Budget 2021 we projected we would meet that commitment one year earlier by 2022/23. This budget confirms that commitment is met this year. Promise made, promise kept.
The savings to taxpayers will accumulate over time to reach, and then exceed, our rollback target. As a result of the cut to the sales tax rate, the indexing of the Basic Personal Amount and personal income tax brackets, removing unnecessary taxes on important services, the elimination of probate fees, and commencing the elimination of education property taxes, Manitobans are saving more of their hard-earned tax dollars.
Under the $2,020 Tax Rollback Guarantee commitments included:
|
Tax Measure |
Implementation Date |
|
Indexing of Basic Personal Amount and Personal Income Tax Brackets |
January 2017 |
|
Retail Sales Tax Rate Reduction from 8 per cent to 7 per cent |
July 2019 |
|
Retail Sales Tax Exemption – Preparing Wills |
January 2020 |
|
Vehicle Registration Fee Reduction – 30 per cent total reduction commitment met in Budget 2022 |
Starting July 2020 |
|
Retail Sales Tax Exemption – Home Insurance |
July 2020 |
|
Retail Sales Tax Exemption –
|
October 2020 |
|
Elimination of Probate Fees |
November 2020 |
|
Retail Sales Tax Exemption – Personal services |
December 2021 |
|
Phasing out of education property taxes |
Starting 2021 |
Building Our Economy
Economic recovery and growth remain at the centre of the government’s plan for a stronger, more prosperous Manitoba.The Manitoba government has worked unceasingly to protect the health of Manitobans. It has also worked to support the health of the economy, which, like economies around the world, was profoundly impacted by COVID-19.
Throughout the pandemic, government met regularly with business organizations representing tens of thousands of workers and every corner of the province to gather input and monitor the impact of the pandemic on the economy.
Feedback from these meetings helped inform the rapid development and implementation of numerous support programs to help businesses cope with and recover from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. More than 80 such meetings have been held to date to discuss pertinent issues and local impacts of COVID-19.
Partner organizations pivoted to respond to the impacts that COVID-19 has had on the business community. Many organizations have supported businesses since the beginning of the pandemic with initiatives such as the development of online toolkits and resources, sourcing PPE and delivery of support programs.
Against this backdrop and given the unprecedented level of disruptions that the COVID-19 pandemic has had on the economy, a renewed and comprehensive effort is needed to coordinate the conditions required to boost Manitoba’s economic recovery – conditions that will lift private-sector confidence and encourage province-wide capital investments.
Economic Development Board of Cabinet
With a focused mandate to improve Manitoba’s economic development activities and increase private-sector investment, a new Economic Development Board of Cabinet was formed in February 2022.
The Economic Development Board of Cabinet will take a whole-of-government approach, with members from all key departments including economic development, investment and trade; finance; advanced education, skills and immigration; Indigenous reconciliation and northern relations; transportation and infrastructure; natural resources and northern development; and agriculture.
The new board and its supporting secretariat will focus on growing the economy through increased investment and expansion of trade, with activities to include:
- increasing private-sector investment and expanding capital availability
-
modernizing government policies, regulations, programs and services to spur economic growth and speed up investment
With a focused mandate to improve Manitoba’s economic development activities and increase private-sector investment, a new Economic Development Board of Cabinet was formed in February 2022.
- expanding local and global market opportunities for Manitoba companies through strategic and targeted trade initiatives
- coordinating cross-departmental economic development activities to reduce delays in investment decisions
- developing market intelligence and analytical capabilities within government
- managing specific business development opportunities
- liaising with the Manitoba business community as stakeholders
A cornerstone of the economic growth strategy is to produce meaningful employment opportunities, as skilled Manitobans are the foundation upon which businesses build success. To help address labour shortages, the Manitoba government will increase investments in education and training, and focus on working with business to attract workers from around the world to fill gaps in labour.
Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy
The Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy, launched in 2021, is foundational to accelerating recovery, advancing Manitoba’s economy and promoting positive outcomes for Manitobans. The pandemic has changed the world and economy in ways that could not have been imagined. Manitoba wants to move forward. The strategy provides the roadmap to economic recovery.
The Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy, launched in 2021, is foundational to accelerating recovery, advancing Manitoba’s economy and promoting positive outcomes for Manitobans.
The goal of the Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy is to ensure people in Manitoba have the right skills, talent and knowledge at the right time, to rebound from the effects of the pandemic and support economic resilience and growth. The strategy was developed through robust engagement and research with over 540 stakeholders. Through this collaborative approach with post-secondary and industry partners, a better Manitoba will be built. Given the disruptions of the pandemic and the labour shortages, the strategy is an important contributor to economic recovery.
Several actions were taken during 2021 in support of the strategy:
- Amendments to the Apprenticeship and Certification Act were announced to modernize the way Manitoba updates Red Seal and provincial training standards to better respond to industry needs.
-
Manitoba invested $50,000 for two initiatives that support women pursuing non-traditional careers:
- Expansion of the Empower program at the Manitoba Institute of Trades and Technology to train women in the information and communications technology industries. The program includes a focus on increasing Indigenous women’s representation
- Support of the Manitoba Construction Sector Council to promote careers for women in the heavy construction industry, in partnership with the River East Transcona School Division
- The Manitoba government invested $8 million in the Canada–Manitoba Job Grant in 2021 – an increase of more than $2 million over 2020 – to give greater access to employee training and to help employers better respond to the impacts of COVID-19.
- In August 2021, the Manitoba government announced an investment of more than $600,000 to partner with the Manitoba Construction Sector Council to deliver a skilled-trades training initiative for Indigenous women in four northern and remote communities. The initiative will provide an opportunity for Indigenous women to acquire valuable skills in a supportive environment, and includes ongoing mentorship during training and throughout their careers.
- In November 2021, the Manitoba government partnered with Economic Development Winnipeg and the Manitoba Chambers of Commerce to launch Retrain Manitoba, a $12.5 million workforce skills development grant program to support economic recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic. The program reimburses employers who invest in retraining for their staff.
Significant work is underway on many of the strategy’s actions. In 2022, through whole-of-government collaboration and key stakeholder consultations, the government will develop potential solutions to address labour shortages in the health sector and other areas:
- partnering with post-secondary institutes to create 400 new nursing seats to meet labour market need
- developing a new post-secondary accountability framework
- reviewing Manitoba’s immigration pathways and streamlining systems
Immigration
Labour shortages have been identified in Manitoba across sectors and within businesses of all sizes. Immigration is an economic driver that can be used to fill labour market needs that cannot be filled domestically. A key factor in post-pandemic economic recovery is the attraction and retention of newcomers. Immigration also supports Manitoba’s post-pandemic economic recovery by addressing skills shortages, attracting international talent and investment, and counteracting out-migration. Budget 2022/23 will help ensure the continuation of this work to support the economy.
Immigration numbers were lower in 2020 as the world locked down. Manitoba welcomed 8,628 immigrants, a decrease of 54 per cent from 2019. Low immigration causes strain on the labour market, tax base, post-secondary sector and economy as a whole. Although the COVID-19 pandemic affected the number of immigrants entering Canada, Manitoba continues to attract skilled workers and business investors from different parts of the globe.
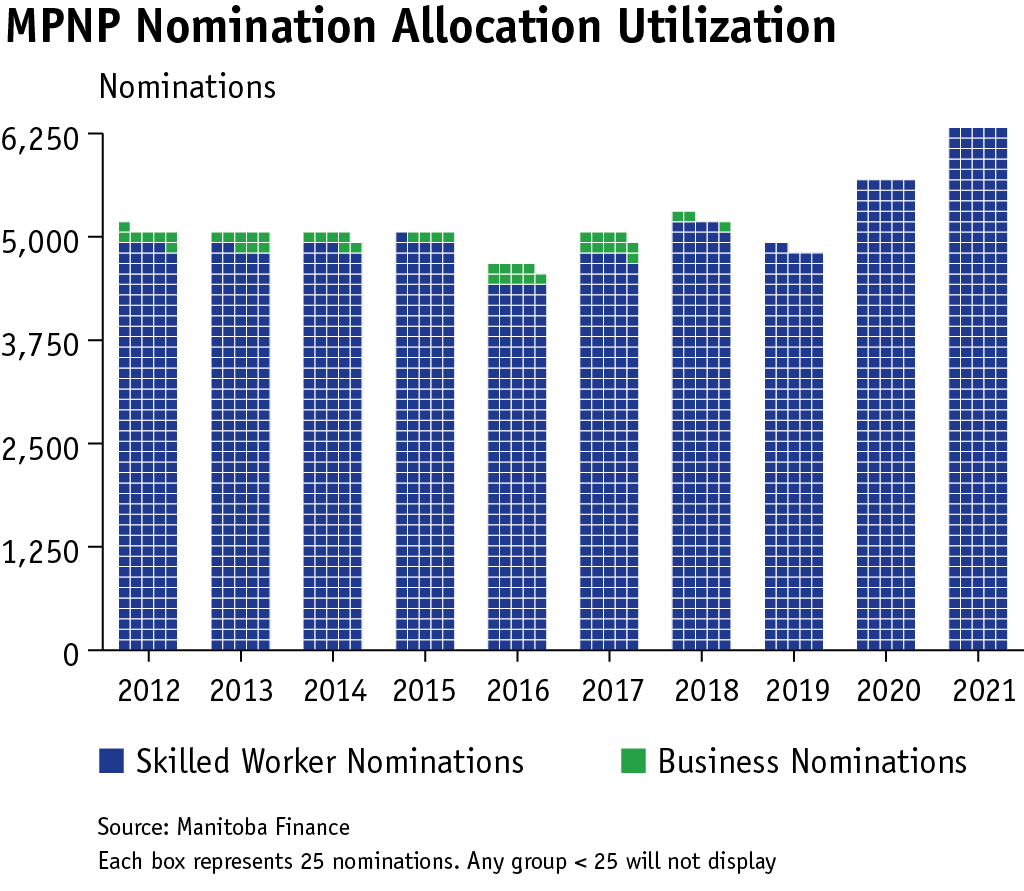
The Manitoba Provincial Nominee Program (MPNP) is critical to supporting Manitoba’s employers, communities and regional labour markets. Once individuals arrive in the province, the government works with a number of settlement service providers to help them safely and successfully adjust to their new environment. In 2021, the program approved the largest number of nominations to date – 6,275. Revenue generated by MPNP application fees are reinvested in services to support the economic and social integration of newcomers throughout Manitoba, including francophone communities, regional hubs and online service delivery, at no additional cost to Manitobans.
The provincial and federal governments are in the process of renegotiating the Canada-Manitoba Immigration Agreement (which has not been renewed since 2003). The objective is to ensure the agreement is responsive and reflective of the current Canadian immigration landscape, impacts by COVID-19 pandemic, responsibilities for settlement and integration services, and the ongoing transformation of Manitoba’s labour market. Manitoba and federal officials have started discussions and are working on the critical path with the targeted completion date of summer 2022.
Revised immigration targets are also under consideration in 2022 with a view to expanding the current program, informed by a new temporary Task Force on Immigration, a group of external stakeholders that will draw from all walks of life across the province.
Manitoba Student Aid
Ensuring access to higher education is foundational to Manitoba’s Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy. Scholarships and bursaries allow more students to access and complete post-secondary education. Government delivers this support through Manitoba Student Aid (MSA), which provides interest-free student loans; the Manitoba Bursary Program (MBP), which offers up-front, non-repayable, bursaries to Indigenous students and low-income students; and the Manitoba Scholarship and Bursary Initiative, which leverages institutional fundraising by providing matching provincial dollars for student awards.
Manitoba Student Aid has received 15,446 applications for nearly $56 million in student loans in 2021. The Manitoba Bursary Program has provided $15 million in government funding and with the support of fundraising this provided a record-level $33 million to nearly 22,500 students with a similar amount anticipated this year.
The government continues to seek opportunities to improve student access to scholarships and bursaries, especially those who are financially disadvantaged, through enhanced promotion to attract matching private-sector contributions and alignment with labour market and community needs.
Access to Venture Capital
Getting the economic recovery right is important for Manitoba’s long-term prosperity. While the economy is steadily rebounding from the depths of the pandemic, Manitoba has not yet returned to its pre-pandemic growth projections. It is imperative for Manitoba to return its attention to strengthening the economy so it can generate the resources that will benefit Manitobans, allowing for further investments to infrastructure and health care, reduce taxes and balance the budget.
Investing in human and financial capital is critical for creating the conditions that will lead to sustainable long-term growth and high-value jobs. The two are linked and both are needed to spur new entrepreneurial activity, innovation and business expansion.
Manitoba businesses have difficulty accessing the financial capital they need to innovate and grow. It is a top concern of Manitoba businesses going forward and is imperative for long-term growth. According to the Canadian Venture Capital and Private Equity Association, from 2018 to 2020 less than one per cent of the total reported value of venture capital investments in Canada occurred in Manitoba, even though Manitoba represents 3.6 per cent of the national economy and population.
The development of a vibrant venture capital ecosystem in Manitoba is particularly important for new start-ups and young entrepreneurial companies that face difficulty obtaining funds to finance business expansion. Small and medium-sized enterprises employ the vast majority of the Manitoban workforce and are the fastest-growing business sector in the province. Manitoba’s economic development path, like its competitors, will be paved by dynamic, high-growth companies led by new innovations and breakthroughs into new markets. The lack of venture capital options for Manitoba businesses puts the province at a competitive disadvantage compared to other provinces whose business communities have greater access to private and government venture funds.
To make Manitoba a more attractive place for entrepreneurship and new economic opportunities available going forward to spur economic recovery as the world emerges from the COVID-19 pandemic, the Manitoba government is committed to proceeding with a venture capital framework.
The new venture capital framework will complement an existing continuum of economic programs that help build the capacity of Manitoba businesses and make strategic investments in industry to generate economic growth.
This includes the Small Business Venture Capital Tax Credit, which was enhanced in Budget 2021 to improve attractiveness for larger investors and provide an earlier return to investors. Effective as of the 2021 taxation year, these enhancements included increasing an investor’s maximum eligible investment to $500,000 from $450,000 and increasing the maximum tax credit claimable against Manitoba income tax in a given year to $120,000 from $67,500. During the 2021 taxation year, Manitoba investors supplied $17.8 million in cash equity to Manitoba businesses under the Small Business Venture Capital Tax Credit, a 92 per cent increase from the pandemic-laden 2020 taxation year.
Further enhancements to the Small Business Venture Capital Tax Credit will be made to benefit Manitobans participating in venture capitals funds, thereby improving access to capital and supporting entrepreneurs.
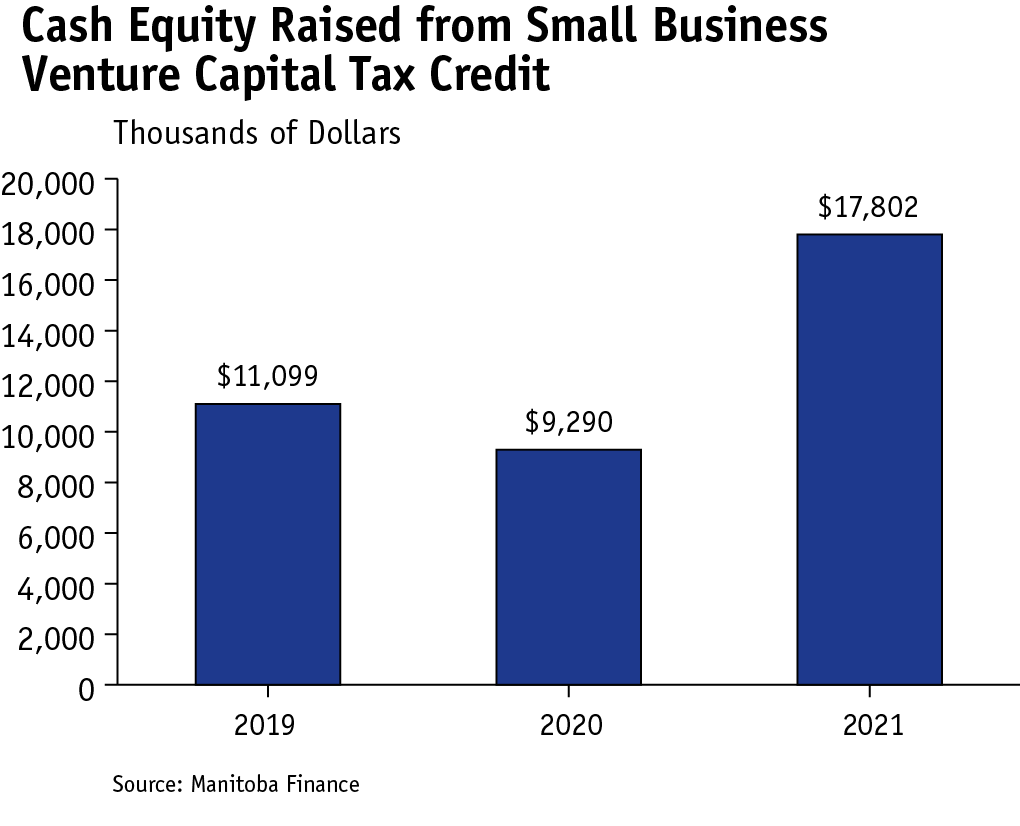
As interest rates increase and debt financing becomes more expensive to fund business growth and entrepreneurship, the importance of access to equity financing will accelerate and the significance of Manitoba’s investor tax credits will be enhanced.
Access to Human Capital
The delivery of employment and training services is central to Manitoba’s economic growth strategy and supporting a high quality of life in the province. Developing partnerships with business and stakeholders will help to create initiatives that address workforce needs and help employers attract and retain the talent they need now and into the future. These services help all Manitobans including the unemployed, under-employed, existing workers, and new labour market entrants to acquire the skills needed to participate fully in the economy.
Working closely with employers, training providers, and community organizations, Manitoba has developed and implemented responsive employment readiness training including essential skills, occupational/sector-specific training, work placement with on-the-job training, and intensive employer and employee workplace supports to support retention. These activities are supporting newcomers and refugees integrate into Manitoba’s labour market, and northern Manitobans train in or near their home communities for jobs in health care and the trades, among others.
Through the Sector Council program, Manitoba partners with sector councils and industry associations in ten key sectors of the provincial economy to develop and deliver sector-wide training in response to employer-identified needs. The program key to increasing employment involvement and commitment to long-term workforce planning.
Companies need access to skilled talent to put their capital investments to use, increase productivity and embark on new opportunities. Without the right workers, Manitoba businesses will continue to be left behind and unable to compete on the global stage.
Investing in skills development, addressing labour shortages through immigration and aligning the education system with the needs of the economy is critical to accelerating the post-COVID-19 economic recovery, advancing the economy and generating wealth and prosperity for all Manitobans.
The Manitoba government has undertaken a number of measures to improve the investment climate in the province, and promote job creation and innovation.
The Interactive Digital Media Tax Credit was enhanced and modernized in 2021 to help continue to grow the burgeoning industry. Manitoba eliminated the tax credit’s expiration date, simplified a company’s initial application for a Certificate of Eligibility, and expanded the tax credit’s eligibility to allow add-on activities, such as downloadable content, ongoing maintenance and updates, and data management and analysis that are complementary to the main products being developed. This has made the tax credit more competitive with other jurisdictions and is serving as an important tool to help attract investment, jobs and growth in the sector.
Introduced in 2019, the Innovation Growth Program encourages small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) private-sector investment to develop and commercialize innovative new products and processes. With cost-shared funding, this supports SMEs in the development and growth stages to de-risk innovative product development, accelerate growth and strengthen SMEs financial position so they can build their business in Manitoba. Since its creation, the program has awarded $2.48 million to support 32 innovation projects.
To help kick-start economic recovery from the pandemic, Manitoba has committed $50 million as part of its Long-Term Recovery Fund, which is investing in worker skills development and digital transformation of Manitoban businesses and will help rebuild consumer confidence.
To help address labour shortages, government is investing in the skills-based economy and working with industry partners to deliver demand-led skills training that will address labour market needs in areas such as hospitality, transportation, manufacturing and the health care sectors. In 2021/22, government made an historic $67 million commitment to invest in the skills training of unemployed and employed workers across the Canada-Manitoba Job Grant, Retrain Manitoba and Skills Development programs.Government will continue to invest in skills training in 2022/23 to help Manitoba move to the next stage of economic recovery.
Agriculture
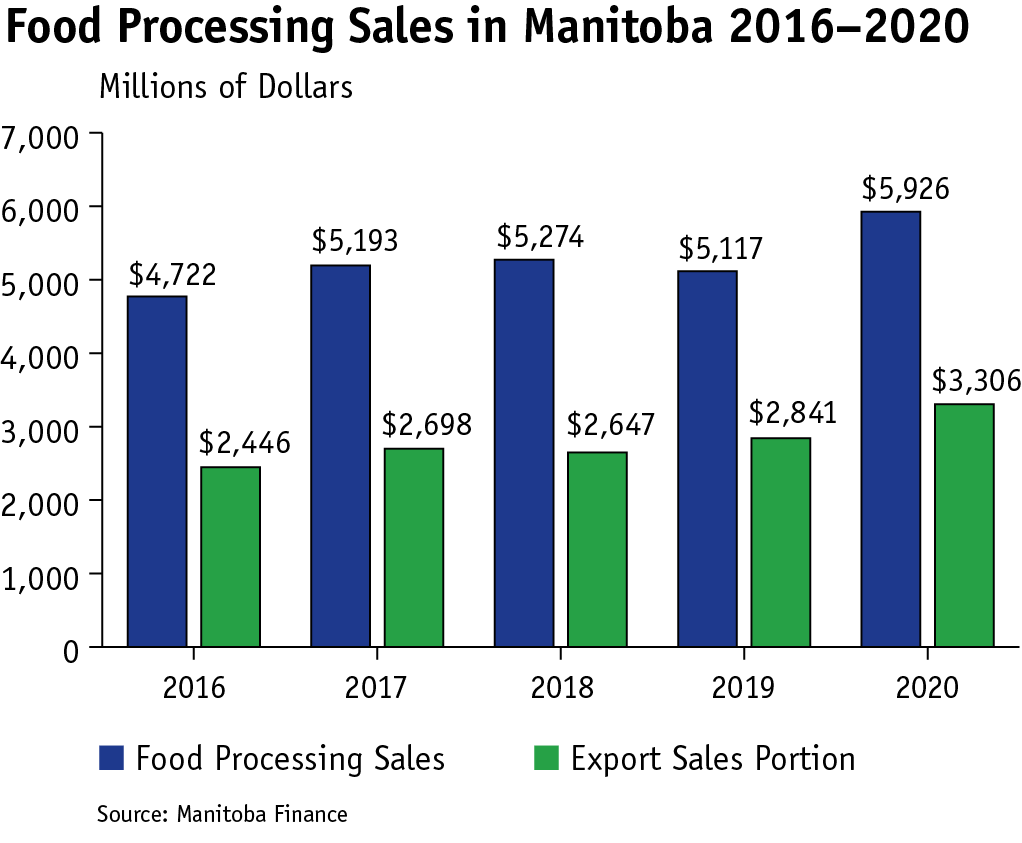
The agriculture and food processing industries are important contributors to Manitoba’s economy and economic health, comprising 7.8 per cent of Manitoba’s GDP and 35,800 jobs in 2020 (5.6 per cent of all jobs in Manitoba). Food processing is the largest manufacturing component, accounting for 32 per cent of Manitoba’s manufacturing value in 2020 (over $5.9 billion, of which $3.3 billion was exported). Processing agricultural commodities grown in Manitoba not only creates new value, but also reduces risk for markets available to farmers when countries close or restrict market access for commodities and in turn, reduces business risk management costs for government.
New and ongoing investment in the agriculture and food processing industries are important to Manitoba to grow and retain economic activity and jobs and to adapt to changing technologies, market conditions, climate change, public expectations, and risks to competitiveness and profitability. New investment demonstrates confidence in the economy and the province is a good place to invest capital for the long term.
Manitoba farms had $48.7 billion invested in land, buildings and equipment in 2020, which is up 5.3 per cent from 2018. These investments are the foundation of successful farming and provide commodities for the food and agriproduct industry.
Manitoba’s food processing industry continued to see strong investment in animal and plant protein projects in 2021 that will support additional processing sales value in the future. Examples include:
- the completion of Merit Functional Foods $150 million canola and pea processing plant (RM of Rosser)
- Maple Leaf Foods investment of $182 million to expand its in-house pre-cooked bacon production (Winnipeg)
- the completion of Roquette’s $600 million pea protein production plant (Portage la Prairie)
- construction in progress on O Foods’ $94 million oat processing plant (RM of Rosser)
- Avena Foods $3 million project over three years to increase pulse processing capacity (Portage la Prairie)
- HyLife Foods Ltd.’s waste-water expansion to support increased pork processing (Neepawa)
- equipment upgrades at Buffalo Creek Mills to support processing and increase export sales (Altona)
Smaller processors are also growing. For example, four provincial meat-processing facilities invested a combined $1.17 million to increase capacity.
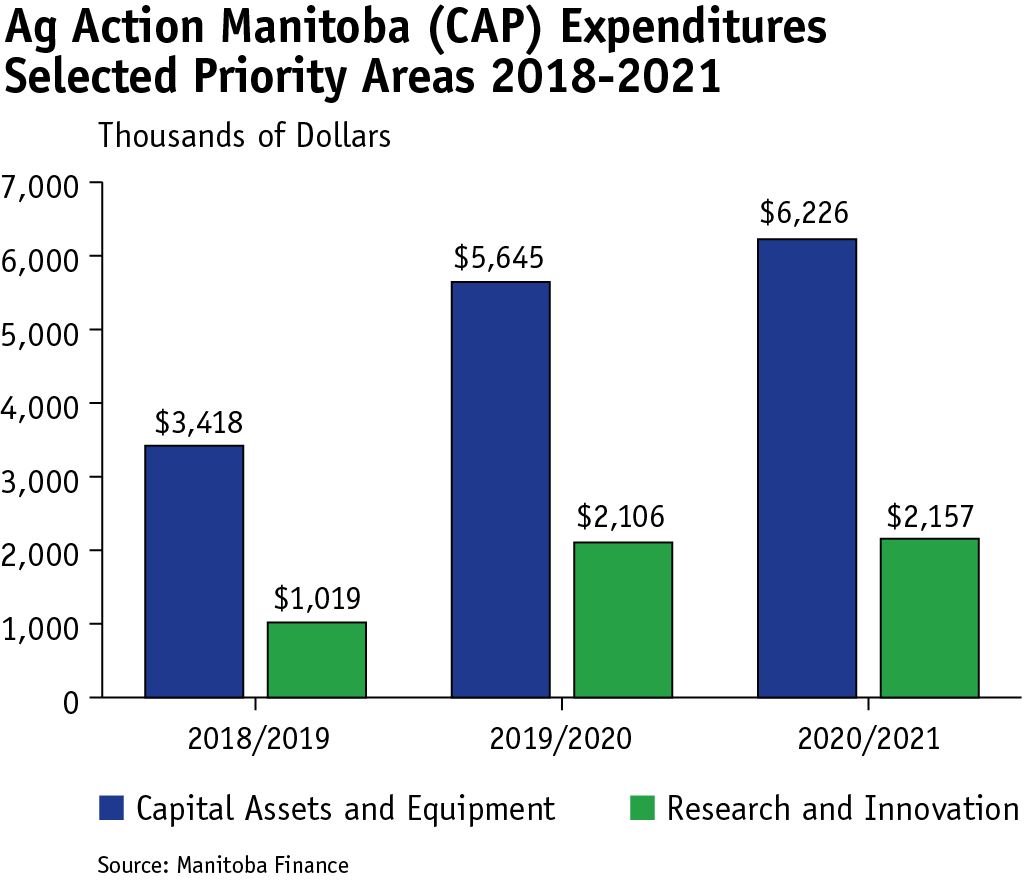
Through Ag Action Manitoba in 2021, Manitoba and Canada provided over $6.2 million to support new and expanded investment in food processing. An additional $2.15 million was provided to support research and innovation for new opportunities, addressing industry challenges and practices to increase environmental sustainability, and to enhance resiliency of Manitoba’s agriculture and agri-food industry.
Manitoba Agricultural Services Corporation is a Crown corporation established with the purpose of supporting and encouraging the sustainability, development and diversification of agriculture and the rural economy of Manitoba by providing insurance, lending, and other programs. To fulfil its mandate, several loan limits are adjusted to account for the changing economic environment in the agricultural sector.
Increases to loan limits represent an important tool to support Manitoba’s economic recovery because of COVID-19 and last year’s drought. The agricultural sector will play a major part in this recovery and ensuring that relevant capital is available is a key component. In addition, Manitoba’s beef herd has reduced because of the recent drought. Stocker Loans are an excellent way to assist in rebuilding herds. The Manitoba Livestock Associations Loan Guarantees Program encourages feeding cattle in Manitoba, which provides direct and indirect jobs and spinoffs for service sectors such as feed suppliers, auction markets, and transportation/equipment dealers.
Manitoba has established itself as a North American leader in processing plant protein ingredients and is poised for additional growth.
Ag Action Manitoba (CAP) Expendatures Selected Priority Areas 2018-2021
Thousands of Dollars
Manitoba has seen significant investment and growth in both plant and animal protein processing, which is being supported through the Manitoba Protein Advantage (MPA). The MPA is a government and industry strategy to attract investment, create jobs and position Manitoba as a preferred choice for sustainably produced plant and animal protein. The plant protein industry is growing exponentially, with opportunities in meat and dairy substitutes as well as alternative proteins (e.g., insects). Manitoba has established itself as a North American leader in processing plant protein ingredients and is poised for additional growth.
Growing standards of living in many countries are driving increased demand for animal protein, with opportunities for additional sales in export markets. Manitoba’s animal protein producers and processors have opportunities to meet this new demand, building on existing production, quality and significant export expertise.
Opportunities are also available to meet the challenges of climate change, environmental sustainability and adding more value to co-products of processing. Examples include renewable fuels, plant-based plastics/packaging, and higher value uses for co-products of plant protein extraction. Development of these products will not only benefit processors, but also farmers as feedstock is needed for renewable fuels. Manitoba also has additional export sales potential, building on a strong pork industry, and plant protein ingredients and consumer products.
A number of factors, many of which are not directly controllable by producers, challenge the agriculture industry. Climate change is a prominent challenge facing farmers and the supply chain for processing. The impacts are not only variable weather, but increased pest and disease risk as temperatures rise and the variability of water available for irrigated crops (such as potatoes and vegetables) and livestock. Other challenges facing both the agriculture and processing industries include labour and skills shortages, trade barriers, new trade competitors, changing consumer preferences (such as reducing meat consumption) as well as water, wastewater and other infrastructure availability.
As the climate changes, the importance of industry, government and academia partnerships increases on research and innovation, risk management, adaptation strategies and surveillance to position industry best to compete. Budget 2022/23 continues Manitoba’s momentum to strengthen the competitiveness, sustainability and resiliency of agriculture and food processing industries in a number of ways:
The government realigned resources in 2021/22 to put more emphasis on climate-change modelling and adaptation. These resources and approach strengthen the modelling of climate impacts and action plans at the agriculture industry level, and supports extension of knowledge at the farm level. This approach will lead to stronger resilience in the agriculture and agri-food industry.
Cross-Sector Support Programs
In addition to sector-focused initiatives, government continued to provide cross-sector supports in 2021 to encourage small and medium-sized enterprises to invest in development and commercialization of innovative new products and to attract capital investments.
The Innovation Growth Program provides support to local businesses that are pursuing innovation and new opportunities, building on Manitoba’s economic strengths. The program had three rounds of awards in 2021, approving total support of $575,000 to six companies. Since inception, the program has approved up to $2.4 million in support for 32 small and medium-size businesses, which are projected to create more than 900 jobs within five years.
The Manitoba Works Capital Incentive encourages businesses to invest and expand in the province by creating a competitive tax environment to help diversify Manitoba’s economy. The program approved six projects in 2021/22, supporting total projected private investment of $491 million.
Throughout 2021, significant cross-sector support programs were implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Key cross-sector support programs introduced or extended in 2021/22 included the Manitoba Bridge Grant, the Manitoba Youth Jobs Program, the Urban and Hometown Green Team Program and the Manitoba Parks Green Team Program, the Manitoba Pandemic Sick Leave Program, the Healthy Hire Manitoba Program and the Sector Support Program.
Additionally, cross-sector programs launched under Manitoba’s $50 million Long-Term Recovery Fund included Retrain Manitoba and the Digital Manitoba Initiative.
Natural Resources and Northern Development
Northern Manitoba
The Look North strategy continues to be a key pillar of Manitoba’s Economic Growth Action Plan. As Look North is advanced, the Manitoba government will also continue to support collaborative approaches and partnerships that will increase Indigenous participation in all sectors of Manitoba’s economy, grow local companies and industries, create jobs, build the necessary skills and talent to attract investment, and increase economic competitiveness.
In March 2021, the Manitoba government allocated over $1 million to grants to support key economic development activities:
- $675,000 was provided to advance commercial fishery certification and to increase market competitiveness for Manitoba’s commercial fisheries.
- $200,000 was provided to improve the viability of Manitoba’s forest sector by encouraging enhanced Indigenous participation in the forest economy.
- Grant funding of up to $150,000 was provided to OneNorth to develop its capacity to leverage assets and actively pursue economic development opportunities related to the Hudson’s Bay rail line.
All four of these initiatives reflect important economic development opportunities for Indigenous and northern Manitobans, helping to position them to emerge from the COVID-19 pandemic in a position of strength.
In July 2021, the Manitoba government invested approximately $3 million in 11 organizations to support key services for Indigenous and northern people in Manitoba. Northern Manitoba organizations funded were Manitoba Keewatinowi Okimakanak and the Northern Association of Community Councils. Provincial organizations that were funded were the Manitoba Association of Friendship Centres, Assembly of Manitoba Chiefs, the Manitoba Metis Federation, the Eagle Urban Transition Centre, Manitoba Moon Voices and Indigenous Languages of Manitoba.
During 2021, government invested $5.1 million to improve infrastructure in several northern communities. This work included water treatment plants, community roads, administrative buildings, waste disposal sites and other projects that significantly impact the well-being of Manitobans living in these communities.
In addition to these projects, 2021 saw the completion of three major water treatment projects, for a total investment of $4.5 million, in northern Manitoba to ensure safe drinking water and improved wastewater management for hundreds of individuals and families living in remote northern Manitoba communities.
The COVID-19 pandemic has reinforced the importance of broadband connectivity and the need to ensure that Manitobans have access to critical and timely information and services no matter where they live, work or travel in Manitoba. In November 2021, the Manitoba government signed a contribution agreement with Xplornet Communications Inc. to provide broadband services to nearly 30 First Nations and approximately 350 rural and northern communities.
Mining
In June 2021, the Manitoba government invested an additional $1 million in the $20 million Manitoba Mineral Development Fund. Established in 2019, the fund plays a critical role in helping to grow and diversify the northern economy. The province has committed to an annual investment of up to six per cent of tax revenues collected from the Mining Tax Act. The additional funds from the mining tax revenue will allow the Manitoba Mineral Development Fund to continue to support northern and Indigenous communities and the mining industry.
In response to industry recommendations to eliminate red tape and to help grow this important sector, the Manitoba government announced in November 2021 that it would introduce multi-year permitting for mineral exploration projects. This will be a valuable benefit to companies pursuing multi-year exploration activities. Work permits for mineral exploration outside of parks will now be valid for up to three years with the option for an additional two-year extension.
Natural Resources and Northern Development is initiating the development of a new Manitoba Mineral Strategy to support and grow the mineral exploration and mining industry in Manitoba, including critical minerals, by encouraging investment, enhancing geoscience knowledge and land use management, and increasing Indigenous participation in all phases of mineral development; as key components of this strategy. Natural Resources and Norther Development will engage exploration and mining industry representatives, local, municipal and Indigenous leaders and communities in the development of this important strategy.
With respect to mineral production, two major corporate announcements were made in 2021:
- In June, Vale announced that it would invest $150 million to extend current mining activities in Thompson by 10 years. The company noted that this was the largest single investment made in the Thompson operations in the past two decades. Beyond the investment in its operations, Vale also noted that it was undertaking aggressive exploration that could extend mining operations past 2040.
- In October, HudBay Minerals announced plans to significantly expand its operations in Snow Lake with the opening of the New Britannia Mill. The New Britannia expansion will include the refurbishing of the gold plant and addition of a new copper flotation facility, ensuring increased production at the Snow Lake operations.
Several announcements were made in 2021 with respect to mine remediation and quarry rehabilitation:
- The province committed $45 million to remediate the abandoned Ruttan Mine near Leaf Rapids.
- The province awarded more than $5.5 million for 55 quarry rehabilitation projects under the Quarry Rehabilitation Program on Private Land and Municipal Land Program.
- The province awarded a $22 million contract to oversee environmental monitoring at several orphaned and abandoned mines under the Orphaned and Abandoned Mine Site Rehabilitation Program.
Forestry
Forestry is a significant economic driver in Manitoba, most notably in the northwest and eastern regions. Manitoba’s forests provide an enormous opportunity for communities and industry stakeholders to explore the economic, social and environmental benefits of this vast resource.
In 2021, there were significant corporate investments in the forestry sector. Market prices for OSB and softwood lumber remained high throughout 2021 and kraft paper prices have been rebounding.
The potential for new forest industry development in Manitoba is strong. Indigenous and northern communities are well positioned for growth in the forest sector. Factors driving a renewed interest in forestry investment include industry innovation, Indigenous partnerships, high commodity prices and the lack of available wood supply in other jurisdictions. Indigenous participation in the forestry sector is essential to ensure everyone benefits from Manitoba’s resources.
In October 2021, Manitoba issued a second two-year option licence to a partnership of four First Nations to explore forest development opportunities on the east side of Lake Winnipeg. In the north, a partnership between industry and seven Nekote First Nations – Nisokapawino Forest Management Corporation – has seen positive results from collaborative resource management planning initiatives.
Investing in Our Communities
Advancing Truth and Reconciliation
The path of truth and reconciliation is the most important journey that must be taken as a province, and as a country, to respond to the injustices of the past.
Manitoba is situated on the traditional lands and territories of the Anishinaabeg, Anishininewuk, Dakota Oyate, Denesuline and Nehethowuk Nations, ancestral lands of Inuit and the homeland of the Red River Métis. As a province, Manitoba continues to benefit from the treaties and relationships with Indigenous peoples, both historical and current.
Indigenous peoples and nations have been subjected to great harm since European contact, resulting in the erosion of culture, language and ways of life. Disparities in socio-economic status, health outcomes and disproportionately high levels of poverty, incarceration and children in care between Indigenous peoples in Manitoba and non-Indigenous Manitobans demonstrate the need for a sustained whole-of-government response. As a province, Manitoba must work to address these wounds and move together down the path of reconciliation.
Manitoba is situated on the traditional lands and territories of the Anishinaabeg, Anishininewuk, Dakota Oyate, Denesuline and Nehethowuk Nations, ancestral lands of Inuit and the homeland of the Red River Métis.
In March 2016, the Manitoba government passed the Path to Reconciliation Act, with unanimous support of the Manitoba legislature. The act sets out the government’s commitment to advancing reconciliation, guided by the Calls to Action of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada and the principles set out in the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (UNDRIP). In 2021, Manitoba introduced amendments to the Path to Reconciliation Act that established the National Inquiry into Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls Calls for Justice as another guiding component of Manitoba’s efforts to advance reconciliation.
COVID-19
Manitoba remains committed to working with provincial and federal partners, Indigenous and northern leadership, partners and stakeholders to continue a timely and consistent response to COVID-19.
The fight against COVID-19 in Indigenous communities continued to evolve as more was learned about the virus and variants as they emerge. Working in co-operation with the First Nations Pandemic Response Coordination Team, First Nation Vaccine Task Force, Urban Indigenous Vaccine Steering Committee, Manitoba Metis Federation and other partners, a variety of measures have been implemented to reduce case numbers, get people vaccinated and keep communities safe. All 63 First Nation communities and all 48 Northern Affairs communities have received allocations of the Moderna/Spikevax™ and Pfizer/Comirnaty™ vaccine for administration to all eligible residents.
Looking forward, the Manitoba Skills, Talent and Knowledge Strategy, a roadmap was launched for the Manitoba government, industry, community, educational institutions and Indigenous organizations to work together to accelerate recovery, advance Manitoba’s economy, and promote positive outcomes for individuals and businesses in the aftermath of COVID-19.
Residential Schools
In May 2021, the heartbreaking tragedy and tragic legacy of residential schools was reawakened across the country with the identification of 215 potential unmarked graves at the former Kamloops Indian Residential School. Canadians were forced to reflect on the fact that children died at these schools and were buried nearby without their families knowing where they were. Indigenous communities are now carrying out the sobering task of identifying potential unmarked graves at former residential school sites across Canada. The numbers being identified are increasing beyond the original estimates of 6,000 children as reported by the Truth and Reconciliation Commission. These sombre events provide a reminder of the tremendous work that lies ahead to address the legacy of residential schools.
On June 21, 2021, Manitoba committed $2.5 million to begin work to find and commemorate children who died attending residential schools.
On June 21, 2021, Manitoba committed $2.5 million to begin the work to find and commemorate children who died attending residential schools. Allocations are being determined through engagements with Indigenous nations, leadership, residential school survivors, Elders and Knowledge Keepers to understand the best use of this funding. Manitoba has been providing technical expertise to those communities who are engaged in active searches upon invitation.
The First Nations, Inuit and Red River Métis Council, comprised of members of key Indigenous governments and community organizations, the National Centre for Truth and Reconciliation, and representatives from the City of Winnipeg and Manitoba and Canadian governments was formed to share information, provide guidance and advice and to develop principles, best practices and resources to support and enhance ongoing Indigenous-led search efforts for children who died attending residential schools.
Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls and 2SLGBTQQIA+ People
Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls and 2SLGBTQQIA+ people is a national tragedy that continues to impact Indigenous communities throughout the country including Manitoba. More than 1,200 Indigenous women and girls in Canada have gone missing or been murdered since the 1980s and for decades, families and loved ones have grieved and called for greater recognition of the crisis of violence against Indigenous women and girls and 2SLGBTQQIA+ people.
In 2017, the Manitoba government passed Bill 221, which proclaims October 4 of each year as Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls Awareness Day.
A broad engagement process involving over 40 community-based organizations is ongoing to inform Manitoba’s response to the National Inquiry into Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls. Engagement with families and survivors is being led by Indigenous organizations with funding support from the Manitoba government. Engagement is essential to ensuring an aligned and effective path forward and is intended to capitalize on Manitoba’s strong, dedicated and vibrant networks that continue to work to put an end to violence against Indigenous women and girls.
Manitoba was an active participant in the development of the federal government’s National Action Plan. The Manitoba government is working to develop a concrete and effective response to the National Inquiry that builds on work that is underway at the community level and aligns with the main pillars of Manitoba’s Framework: Addressing Gender-Based Violence . The government recognizes that this response is a starting point from which the ongoing work will evolve and grow over time.
In the meantime, Manitoba is pursuing a wide variety of more immediate activities that align with the Calls for Justice , and support efforts to end violence against Indigenous women and girls. In 2021, Manitoba provided over $50,000 in partnership with community organizations to honour and acknowledge missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls. Several events and initiatives occurred to honour missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls and 2SLGBTQQIA+ people including the Wahbung Abinoonjiiag Soles on Fire Walk/Run and the unveiling of Sacred Spirits of Turtle Island, a permanent outdoor art installation at the Gaynor Family Regional Library in Selkirk. A website has been built dedicated to the issue of missing and murdered Indigenous women and girls and 2SLGBTQQIA+ people to ensure Manitobans can stay up to date, share resources and further educate themselves on the matter.
Child Welfare
The federal Act Respecting First Nations, Inuit and Métis children youth and families (S.C. 2019, c.24), provides a framework for Indigenous governing bodies, communities or peoples to exercise their jurisdiction over child and family services (CFS) for Indigenous children and families, in alignment with national standards for provision of care. The federal Act enables Indigenous-governing bodies to pass laws related to the provision of CFS on and off reserve.
The safety and well-being of Manitoba children, youth and families and building a foundation for success is a priority for this government.
Manitoba is working with various partners to ensure that the federal Act is implemented in a way that prioritizes child safety. The safety and well-being of Manitoba children, youth and families and building a foundation for success is a priority for this government.
Manitoba supports Indigenous peoples’ right to self-governance and recognizes that this is an important aspect of reconciliation. The government is working with Indigenous leadership to assist in the effective transition to full Indigenous jurisdiction over Indigenous CFS.
In response to Call to Action #5 regarding culturally appropriate parenting resources for Indigenous families, Manitoba provided more than $1.2 million in partnership with Mount Carmel Clinic and Granny’s House to provide culturally appropriate services and work to keep families together.
Over the past year, Manitoba has implemented many initiatives, partnered on numerous community programs and projects, and taken many steps to advance truth and reconciliation, guided by the Calls to Action , the principles of UNDRIP and the National Inquiry&aposs Calls for Justice . A collection of these initiatives addressing specific matters are outlined below. For further information about Manitoba’s progress and work to advance truth and reconciliation, read The Path to Reconciliation Act Annual Progress Report , available on Manitoba Indigenous Reconciliation and Northern Relations’ website.
Truth and Reconciliation in the Educational System
In keeping with the Manitoba government’s commitment to truth and reconciliation, we acknowledge the important role that education and schools play to ensure Manitobans collectively take time to think about, learn about, honour, and remember those who attended residential and day schools and those who did not come home. Mamàhtawisiwin – The Wonder We Are Born With is a new policy framework for Indigenous education that outlines guiding principles and actions for achieving the intended learning outcomes for First Nations, Métis and Inuit students and for all students in Manitoba.
Building upon the pilots launched in 2021/22, Manitoba is investing $1.6 million in the Elders and Knowledge Keepers in Schools Initiative to engage over 40 Elders and Knowledge Keepers in sharing histories, languages and cultures, traditional values, contemporary lifestyles and traditional knowledge in the provincial curricula. In addition, additional investments towards professional development for teachers and school staff will further treaty education and anti-colonization/anti-racism, mental health, and inclusive mindsets and practices about Indigenous ways of knowing, being and doing.
National Day for Truth and Reconciliation
September 30 is the National Day for Truth and Reconciliation. In 2021, the Manitoba government marked the inaugural national day in several ways. The Manitoba public service recognized the federal statutory holiday through the closure of non-essential government services and offices for the day. This provided public servants the opportunity to recognize the history and impacts of residential schools. The flags were lowered to half-mast on all provincial government buildings and the Manitoba Legislative Building was lit in orange.
Manitoba provided $200,000 in partnership with seven Indian Residential School Healing Centres to provide culturally appropriate healing and wellness supports to survivors of residential schools, families and communities.
Manitoba also worked in collaboration with the National Centre for Truth and Reconciliation and the Manitoba Museum to hold events for Manitobans and Canadians to learn and reflect on the history and legacy of residential schools, honour the survivors, remember those who did not come home and spread the message that every child matters. Over $125,000 was dedicated to these events and initiatives.
Call to Action #57
Call to Action #57 calls on all levels of government to provide training and educational opportunities for public servants to enhance their learning on topics related to Indigenous history, rights, and reconciliation. The Manitoba government is dedicated to advancing reconciliation, and empowering its vibrant public service to find new and innovative ways through which truth and reconciliation can be pursued.
In addition to a number of ongoing learning opportunities, in October 2021, Manitoba introduced a conversation series among public servants to discuss experiences and understandings of reconciliation, and opportunities to advance truth and reconciliation throughout government. This series was facilitated by Clear Direction, an Indigenous consultation and facilitation group dedicated to helping instill the Principles of Reconciliation into everyday practices.
Manitoba provided $25,000 in financial support to Circles for Reconciliation, a group that aims to create trusting and meaningful relationships between Indigenous and non-Indigenous peoples. Through the initiative, the group facilitates ‘circles’ for public- and private-sector organizations and groups, on various themes such as the meaning of land for Indigenous people, residential schools, intergenerational trauma, the pass system and the ‘60s Scoop.
Treaty Relationship
2021 marked the 150th anniversaries of Treaties 1 and 2, the first of the numbered treaties to be signed in Canada. To mark this important occasion in Manitoba’s shared history, the treaty flags were raised in Memorial Park and ceremonies were held. This anniversary provided a welcome opportunity to reflect and celebrate the treaty relationship with First Nations, and recommit to being good treaty partners.
On November 29, 2021, the first, historic reading of a land acknowledgment occurred to commence house proceedings in the Manitoba legislature. The land acknowledgement was developed in collaboration with Indigenous leadership, and was unanimously agreed to by all three political parties. Manitoba is taking the necessary steps to codify formally the land acknowledgement into the opening process.
Treaty Land Entitlement (TLE) continues to be a priority for Manitoba and one of the most important ways through which reconciliation is pursued. There are nine TLE agreements in Manitoba covering 29 Entitlement First Nations for a total of approximately 1.423 million acres of Crown land and acquisition land. Manitoba Indigenous Reconciliation and Northern Relations has allocated $500,000 as part of a renewed approach to advancing TLE.
Four new urban economic development zones have been created with Waywayseecappo First Nation, Gambler First Nation, Sapotaweyak Cree Nation, and Peguis First Nation. Additionally, the seven First Nations of Treaty 1 are in the midst of the urban reserve creation process at Naawi- Oodena, the former site of the Kapyong Barracks in Winnipeg. Manitoba eagerly anticipates Naawi-Oodena as a unique opportunity to advance economic reconciliation with First Nations and economic opportunities for all Manitobans.
The Indigenous Reconciliation Initiatives Fund
Reconciliation is crucial to advancing progress on economic growth and the collective and personal equalities related to socio-economic well-being and health outcomes for Indigenous peoples and all Manitobans.
Starting next fiscal year, a $5 million allocation will be made to advance progress on reconciliation achieved through relationship building activities as guided by the principles of respect, engagement, understanding and action in Manitoba’s Path to Reconciliation Act. The activities include but are not limited to:
- enhancing partnerships with Indigenous communities across sectors like health, education, business and industry
- maintaining and strengthening connections with Indigenous cultures, languages and ways of life.
- building supportive and safe community networks that promote diversity and inclusion
- addressing the harms left by the tragic legacy of residential schools
- decreasing knowledge gaps on the past and present experiences of Indigenous peoples in Manitoba
- actions that respond to and go beyond the Calls to Action of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission of Canada, the principles set out in the United Nations Declaration of the Rights of Indigenous Peoples, and the Calls for Justice of the National Inquiry into Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls
This funding may apply to other strategic purposes for Indigenous groups, communities and governing bodies to advancing meaningful dialogue and negotiation with the federal government and other levels of government including municipalities to address historic injustices faced by Indigenous peoples.
Manitoba Indigenous Reconciliation and Northern Relations will administer and oversee these resources that will be made accessible to all government departments to support related initiatives that advance progress on reconciliation.
Investing in Our Communities
Improving Education
Manitoba is committed to strengthening and improving public education.
Early Learning and Child Care
Manitoba continues with significant investments to modernize early learning and child care, building a stronger and more responsive system to ensure high-quality, affordable and accessible services for all families and to advance Manitoba’s economic growth by supporting parents to participate in the workforce.
As part of these modernization efforts, Canada and Manitoba finalized the Canada-Wide Early Learning and Child Care Agreement in December 2021 with $267 million available in 2022/23. One of the first key joint initiatives to be implemented is an increase to income thresholds to help grow the number of Manitoba families that are eligible for a child care subsidy. The expansion of eligibility for child care subsidy will result in an increase of approximately 28,600 children to receive financial assistance to access early learning and child care services. While federal funding supports children from newborns to age 6, provincial funding of approximately $18.2 million will support the growing number of eligible children aged seven to 12 to access a child care subsidy for after-school child care programs.
The expansion of eligibility for child care subsidy will result in an increase of approximately 28,600 children to receive financial assistance to access early learning and child care services.
Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education
Extensive engagements have taken place since the March 2021 release of the 75 recommendations from the Commission on Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education report, Our Children’s Success: Manitoba’s Future. These consultations have resulted in the decision not to proceed with Bill 64, which proposed significant changes to the school trustee model and reaffirmed many shared priorities and opportunities for continuous improvement, both of which require a focus on existing strengths and working together as a system.
In 2022/23, the province will launch work to solidify the future of remote learning across the province.
Manitoba’s kindergarten to Grade 12 education roadmap will guide the path forward, along with a new Manitoba Inter-Sectoral Education Council, to inform provincial, local and school-level planning. The Council will provide strategic leadership and oversight to the development and implementation of a comprehensive Provincial Education Action Plan in alignment with the vision, mission, guiding principles and pillars for student success set out in the roadmap.
The Manitoba government does know that education programming, services and supports can vary depending on where students live. In response to the Commission on Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education, consultations are underway to develop a new equitable funding model. The goal is to have the initial components of the new formula in place for September 2023 including an updated special needs funding model.
While the government looks forward to advancing its work toward equitable outcomes for all students, it remains focused on keeping schools safe and open for continued in-person learning as part of the COVID-19 response. In 2021/22, Manitoba made available $63 million in the Safe Schools Fund to ensure continued learning for students and worked closely with public health officials and the kindergarten to Grade 12 education system to implement preventive measures and contingency plans to keep students and staff safe. The funding includes close to $52 million to address the impacts on learning and well-being and putting health and safety measures in place, including: ventilation improvements, $6 million for masks and personal protective equipment, and $5 million to improve access to remote learning. Although the government knows that students learn best in classrooms and commits to the priority of in-person learning, virtual learning offers increased access for many students.
Student Engagement and Well-being
Keeping students and parents engaged is critical to moving forward. A new Student Advisory Council will inform this path forward, along with the following:
Funding for Schools
Over $3 billion is spent on kindergarten to Grade 12 education. In 2020, the Manitoba government established a $1.6-billion guarantee for education funding over four years including investments in operating and capital funding.
Budget 2022 means that $512.2 million has been invested toward this funding guarantee. This includes $307.9 million in capital allocated toward building two more schools under the commitment to build 20 new schools, along with renovation and addition projects in existing schools.
By the end of 2022/23, 10 of the 20 new schools will be open or under construction. Others are in the purchase and design processes.
The Manitoba government has put in place a funding model review team to guide the development of a new education funding model and has begun consultations with school divisions and key education stakeholder organizations. The funding model will establish a better process for education funding, one that supports long-term planning and gives schools and regional leaders the flexibility they need to address local needs. Building on the findings of the Commission on Kindergarten to Grade 12 Education, these consultations will ensure input from stakeholders on what they need to address differences in programming and ensure equity in funding across the province, particularly in rural, remote and northern communities.
By the end of 2022/23, 10 of the 20 new schools will be open or under construction. Others are in the purchase and design processes.
Investing in Our Communities
Social Services and Families
The Manitoba government is committed to protecting and promoting the well-being of all Manitobans, especially the families and individuals who are most in need of support.
Provincial Homelessness Strategy
Preliminary evidence from 2021 indicates that while the total number of people experiencing or at risk of homelessness has remained stable, there are significantly more people now categorized as unsheltered. People experiencing homelessness are disproportionately Indigenous, and at least 50 per cent identify as having previously been involved with the Child and Family Services system.
The strategy includes an emphasis on homelessness prevention and Indigenous-led responses, increasing the availability of housing with supports, modernizing the government’s emergency response, developing seamless service delivery systems, and understanding the different nature of homelessness in rural and northern Manitoba. The strategy is underpinned by a commitment to a whole-of-government approach, aims to end homelessness, is informed by Indigenous and community perspectives, and incorporates the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic.
Please refer to Poverty Reduction Strategy budget paper for further information on other programs and initiatives the government is implementing to address homelessness in Manitoba.
Community Living disABILITY Services and Children’s disABILITY Services
Throughout the pandemic, the adult disability services sector demonstrated exceptional strength and resiliency to ensure that vulnerable adults continued to receive services in the community. The challenges of this past year also highlighted opportunities where the government can continue to work with service delivery partners to strengthen the Community Living disABILITY Services (CLDS) program and innovate for the future.
Building upon recent investments of $1.1 million toward the Innovation and Transformation Fund and the Quality Assurance Pilot Project, CLDS will continue to work with the disability services sector to support agency capacity and sustainability, as well as work toward improved outcomes for Manitobans supported by the program.
The Manitoba government remains committed to improving the outcomes of children with disabilities in Manitoba. Over 6,000 children and their families access the Children’s disABILITY Services program and it is anticipated the demand for supports will continue to grow. Over the past five years, caseloads have increased 19.8 per cent from 2015/16 to 2020/21, outpacing a growth rate of 11.4 per cent over the five years prior.
To ensure that both the Community Living disABILITY Services and Children’s disABILITY Services programs can continue to remain sustainable and address the needs of Manitobans for years to come, the Department of Families will continue identifying opportunities for innovative service delivery and ensure the right level of services are provided at the right time.
Employment and Income Assistance Transformation
Over the past year, the Department of Families has undertaken significant work to transform Employment and Income Assistance (EIA). The program is being transformed from fostering dependence to creating meaningful bridges to employment for Manitobans while having support for people with severe and prolonged disabilities. The department has launched new programming and tools to improve client engagement efforts including:
- establishing service delivery standards in the EIA Case Management Framework
- improving utilization and management of client data to improve service
-
developing the EIA Agency Awareness Tool, which is a repository of available community resources and funded agencies that EIA staff can refer to supportively plan with clients
The program is being transformed from fostering dependence to creating meaningful bridges to employment for Manitobans while having support for people with severe and prolonged disabilities.
In 2021/22, the Manitoba government partnered with Opportunities for Employment to provide three new programs to support EIA Transformation:
- The Single Parent Employment Program, which provides employment supports and child care services to single parents with young children.
- The Community Home Support Program, expanded to support single parents, which provides pre-employment training and community-based work during flexible hours.
- The Supported Employment Program, which provides pre-employment and employment supports to clients with multiple barriers, adopting a supported employment model.
In 2022/23, EIA Transformation will focus on diversion programming, by providing rapid response programming to clients applying for supports, employment and training programs for Indigenous youth, and enhanced employment programming in rural and northern regions of the provinces.
New Income Support Program for People with Severe and Prolonged Disabilities
In October 2021, the Disability Support Act and related amendments to the Manitoba Assistance Act received royal assent . The new legislation established a framework for the new income support program for people with severe and prolonged disabilities. The new program is separate and distinct from existing programs and benefits offered by the Department of Families including EIA.
The development of the new program has consisted of extensive consultations with jurisdictions across Canada, within the government of Manitoba, as well as community partners across Manitoba. More details on the new program will be available throughout 2022/23.
Family Violence Prevention Program Funding Model
The Family Violence Prevention Program (FVPP) supports the operation of 10 family violence shelters across the province. In the November 2021 speech from the throne, Manitoba committed to expanding funding for family violence shelters and other key supports. During 2021, FVPP developed an improved funding model for the family violence shelter sector to meet this commitment. The proposed $5.1 million increase, over three years, will work to build capacity across the sector to ensure that Manitobans experiencing family violence receive effective and timely support across the province.
Supporting Skilled Trades for Women
Manitoba Status of Women has invested $1.1 million in training initiatives for women in under-represented areas. A key principle in these programs is the importance of representation, mentorship and community-based training, ensuring a greater likelihood of success for students. These programs, connected with employers and industry representatives are delivering strong outcomes.
Manitoba Status of Women has invested $1.1 million in training initiatives for women in under-represented areas.
An initiative with the Manitoba Construction Sector Council that provides community-based training and mentorship supports for Indigenous women launched in spring 2021. Skilled trades training in the areas of framer and blaster driller have been completed in Pinaymootang and Pimichikamak respectively. Black Hole Driller training began in War Lake/York Landing in February 2022, Water and Waste Water Wystem Installer training is set to begin in early 2022 in Dakota Tipi when COVID-19 permits. In the first two cohorts, 21 women graduated and are fully employed in their communities, noting they would not have pursued this activity if it were not delivered in their home community. Based on the success of these initial cohorts, additional sessions will be offered in Pinaymootang and Pimichikamak, bringing the total training investment in these communities to $819,000.
Manitoba Status of Women also recently made an agreement valued at $285,000 with Manitoba Aerospace to provide skills training to up to 15 women in gas turbine repair in partnership with StandardAero. The program will include regular classroom instruction, work-integrated learning on site at StandardAero and a job coach to support the women throughout the program and their transition into the workplace. Upon successful training completion, StandardAero will offer permanent, full-time employment to all trainees.
Child and Youth Services
Community Care providers provide residential care to many high and complex needs children and youth in care of child and family services agencies. COVID-19 has exacerbated longstanding recruitment and retention challenges for Community Care Provider organizations. To address these challenges, the province of Manitoba is committed to increase funding by $4.91 million annually for salaries and benefits of frontline staff. This funding will provide flexibility to Community Care Providers to determine how best to respond to critical staffing pressures. This funding will also help ensure continued quality of care needed to support positive outcome achievement for vulnerable children and youth.
Housing
Manitoba Housing has been actively working with all levels of government to address the impacts of COVID-19 on vulnerable populations, including those experiencing homelessness. A $5.6 million Manitoba Rent Relief Fund was launched in June 2021, in partnership with the Manitoba Non-Profit Housing Association (MNPHA), to provide support for low to moderate income Manitobans to help secure, maintain or stabilize housing. Manitoba also provided $2.56 million to MNPHA for projects in Winnipeg over the next two years to transition persons experiencing homelessness into stable housing environments.
In 2022/23, Manitoba Housing will prioritize National Housing Strategy funding to help the most vulnerable households access housing and achieve stable tenancies. Specialized housing and supports will target those at risk of or experiencing homelessness, youth aging out of care, Indigenous Manitobans, women and children fleeing violence, and other vulnerable groups as they transition through life circumstances.
COVID-19 Response
The government has worked to provide support for families and workers affected by the pandemic including:
- ensuring critical services workers and their children can access child care
- continuing to provide licensed child care centres with their full operating grants and subsidies, providing funding to offset the loss of parent fees due to closures or reductions in service (over $2 million in 2021/22), and waiving the subsidy program’s allowable absent days for COVID-19 related issues
- extending and expanding eligibility for the $1.6 million Pandemic Staffing Support Benefit to help address urgent staffing needs of service providers to the disabled, child care centres, child welfare and emergency shelters
- since the beginning of the pandemic, providing $8.4 million in personal protective equipment for its sectors including masks, gowns, eye protection, gloves and hand sanitizer
- supplying rapid antigen test kits for service providers, front-line government staff and vulnerable populations
- supporting Community Living disABILITY Services and Child and Family Services providers with nursing consultation to manage suspected and confirmed cases of COVID-19 in their facilities
- providing regular updated guidance to service providers in line with public health orders
- facilitating access to vaccination for vulnerable groups including Children’s disABILITY Services, Community Living disABILITY Services participants and Employment and Assistance clients
- investing in the Home Nutrition and Learning Program to provide consistent, quality meals to children who are at risk of food insecurity because of the COVID-19 pandemic
- supporting the homelessness sector with over $8 million to support isolation units, additional shelter capacity, rental units and case management for homeless youth, and emergency meals
- Youth transitioning out of care are among those who are most negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. The Province of Manitoba is committed to grant funding of up to 1.5 million on a one time basis to extend existing supports to young adults who would otherwise be ineligible for ongoing supports from Child and Family Services (CFS) agencies, until March 31, 2023. This includes young adults who were non-permanent wards and those Agreement with Young Adult participants aging out at 21, to help ensure a successful transition to adulthood during this unprecedented time. With this funding, these youth are able to continue receiving supports such as financial assistance, housing, and mental health services.
Manitoba’s Poverty Reduction Strategy
Please see the Budget 2022 paper Manitoba’s Poverty Reduction Strategy for additional information on the government’s work to address important issues in the areas of employment, early learning and child care, income assistance, mental health, community-based projects, and social innovation.
Investing in Our Communities
Building Municipal Partnerships
The Manitoba government recognizes that in today’s interconnected world, it needs to work with its municipal partners to ensure strong and healthy communities. Large-scale and complex challenges facing cities, towns and rural areas require many levels and forms of collaboration that result in creative solutions.
Municipal partnerships leverage collective action, broaden resources and investments available for achieving common goals, result in new ideas and innovative solutions, improve decision-making and information sharing, and increase collaboration when diverging interests are involved. Ultimately, they result in better outcomes for Manitobans – outcomes that could not have been achieved if the provincial government or municipalities acted alone.
Government continues to establish collaborative processes with municipalities to strengthen provincial-municipal growth and partnership opportunities. These opportunities include:
- Broadening and maximizing investments to modernize and expand water and waste-water systems across Manitoba in order to grow regions and communities while protecting water quality and the health of Lake Winnipeg. This includes specific investments to upgrade the City of Winnipeg’s North End Water Pollution Control Centre.
- Continuing to prioritize investments in other green growth and infrastructure. The Manitoba government has committed to invest in 8 municipal green infrastructure projects under the Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program. This includes funding support for water pollution control facility upgrades in Portage la Prairie, and a regional waste-water project in the Morden/Stanley/Winkler region. Manitoba is also working with the City of Winnipeg for new zero-emission electric bus infrastructure.
- Supporting economic growth for municipalities through streamlined and more certain planning and permitting processes and supporting municipal collaboration within the capital planning region.
- Assisting municipalities to mitigate against future flood and drought events related to climate change through initiatives such as the Mitigation and Preparedness Program.
- Collectively supporting pandemic response and related recovery.
Over the past year, the Manitoba government established individual working group tables on collaboration with the City of Winnipeg, the Association of Manitoba Municipalities (AMM), the Association of Manitoba Bilingual Municipalities (AMBM) and the Manitoba Municipal Administrators’ Association to further outcomes on these opportunities. These partnerships have resulted in:
- Direct input into ongoing municipal operating and infrastructure funding needs. This includes advice on the development and administration of several municipal funding support programs including the operating and capital baskets, the Municipal Service Delivery Improvement Program, the Mitigation and Preparedness Program, and the Building Sustainable Communities Program.
- Enhanced discussions with the City of Winnipeg to improve practices in areas of mutual interest including permit processes and red tape reduction, municipal funding and fiscal transparency, and property assessment services.
- Continued annual provincial support for the Canada-Manitoba Agreement on French Language Services, in partnership with the AMBM.
- The proclamation of the first-ever Municipal Government Awareness Week in recognition of municipalities’ exceptional dedication to service Manitobans.
The government also leveraged municipal partnerships to support the diverse needs of municipalities as they dealt with the COVID-19 pandemic. This includes the Municipal Enforcement Support Program, facilitating the distribution of COVID-19 public health information and reducing costs through common procurement of protective equipment to municipalities. Regular calls with municipal administrators were established to manage the pandemic’s impacts on municipal operations. Based on the positive feedback on the value of these calls, work is now underway to transition from a pandemic-focused form of engagement to customer-focused engagement with municipal administrators to share good practices on a broader range of issues that ultimately reduce costs and improve services on the front-line in communities.
Budget 2022 includes a 26.4 per cent increase in the annual Manitoba Water Services Board budget to $20 million from $15.8 million to support municipal water and sewer projects, and continued funding support for federal-provincial programs, notably the Investing in Canada Infrastructure Program.
Investing in Our Communities
Investing in Sports, Culture and Heritage
The sport, culture and heritage sectors continue to endure among the biggest impacts from COVID-19, given the restrictions on public gatherings and travel.
Manitoba and other levels of government have provided supports in these sectors throughout the pandemic, contributing to organizational stability and resilience that will facilitate a safe restoring of services. The Manitoba government will continue to engage with the many stakeholders to ensure that investments promote a successful recovery and the 2019 Our Way Forward: Manitoba’s Culture Policy and Action Plan will help guide this effort.
Manitoba’s Film and Video Production Sector
The film and video production industry continues to be a key economic driver and vital contributor to the province’s creative community, projecting a total production volume of nearly $300 million in 2021/22. Government’s continued investment in this sector has ensured that Manitoba production companies, the companies that service the industry and the over 2,500 professionals involved in the industry, have continued to work throughout
the pandemic.
Budget 2022 preserves Manitoba’s investments in the film and video production sector facilitating its continued contribution to jobs, economic growth and a strong creative sector. These investments include making the Film and Video Tax Credit program permanent in 2019, enhancing the Cost-of-Production Tax Credit with an eight per cent Manitoba Company bonus in 2020, and adapting the 10 per cent Frequent Filming bonus on the Cost-of-Salaries Tax Credit to remain effective during production delays resulting from necessary health restrictions.
Continued investment in the cultural industries ensures that book publishing and book printing remain active creative and economic contributors to Manitoba. The Book Publishing Tax Credit was made permanent in 2021.
Arts and Culture Sustainability Funds
In 2020/21, the Manitoba government invested up to $6 million in one-time funding to support areas of the arts and culture sector severely impacted by COVID-19 related facility closures, programming and event cancellations, and significant loss of revenues and jobs.
Funding was allocated to the Manitoba Arts Council (MAC) and Manitoba Film and Music (MFM) for distribution to eligible artists and organizations. In 2021/22, MAC and MFM committed all available funds through 175 grant awards to arts and cultural organizations and professional music industry companies and 90 grant awards to artists. An additional $6 million was provided through the Arts and Culture Sustainability Fund in 2021/22 to continue to support the sector in 2022.
The Arts and Culture Sustainability Funds have helped to stabilize organizations and supported the adaptation of operations, programming and artistic practices to ensure a more resilient and sustainable arts and cultural sector.
To further promote a vibrant and sustainable sector, Budget 2022 introduces a new Arts, Culture and Sport Community Fund. Manitobans working in this sector, and the many more who enjoy and celebrate Manitoba&aposs rich culture, will benefit from this enhanced support for capital projects and programming related to arts, culture, and sports initiatives.
With $100 million committed over three years, from 2022/23 to 2024/25, this fund will address needs across the sector for capital projects, capacity building, community festivals, and events in Manitoba.
Tourism and Hospitality
Manitoba’s tourism and accommodation sector – a key contributor to the province’s economy – was impacted significantly by a reduction in domestic and international travel and other restrictions that were necessary to protect Manitobans and all Canadians from the spread of COVID-19.
To provide financial relief and support the sustainability of the sector through the pandemic, the Manitoba government invested $8 million for the creation of a new Hospitality Relief Sector Program. The program was administered by the Manitoba Hotel Association and the Manitoba Lodges and Outfitters Association.
The province also waived the 2021 annual permit and licence renewal fees for resource tourism operators, to reduce their financial burden caused by ongoing COVID-19 restrictions.
During the Pandemic, the government provided $9 million to the Dine-in Restaurant Relief Program, administered by the Manitoba Chambers of Commerce in partnership with the Manitoba Restaurant and Foodservices Association. The program helped offset delivery costs for dine-in restaurants that shifted to a delivery model due to public health restrictions.
With an emphasis on destination management, Travel Manitoba will support tourism businesses and communities by providing advice, funding and training that will result in the development of new and enhanced tourism experiences and destinations. Through its Tourism Innovation and Recovery Fund, Travel Manitoba supported 50 tourism businesses with over $1 million in their efforts to recover from the effects of the pandemic by adapting to changing customer expectations and offering innovative experiences. Projects receiving support included many in the eastern, northern and western parts of the province, as well as the Interlake and Winnipeg.
In October 2021, Premier Stefanson spent several days visiting northern Manitoba, meeting with local officials, business leaders and community members in Thompson and Churchill to discuss current pandemic challenges and plans for a strong economic recovery. As part of an effort to encourage international travel to northern Manitoba, a small delegation of foreign diplomats stationed in Canada and tourism professionals joined the premier in Churchill to learn about and promote the community internationally.
In the summer and fall of 2021, the government supported the Tourism Recovery Incentive Program (TRIP). Administered by the Manitoba Chambers of Commerce, the program encouraged Manitoba residents to take a staycation and provided a rebate of up to $100 on a one-night stay at an accommodation or resort of their choice, and 50 per cent off entry to any of Manitoba’s “Star Attractions”. Over 25,000 Manitoba residents received more than $2.2 million in rebates. The total sales to Manitoba’s hotel and attractions were over $5.5 million. The program is scheduled to run again May 6–16, 2022.
The Bay Building Fund
In Budget 2021, the Manitoba government established the $25 million Bay Building Fund to support projects that will restore, preserve or maintain the heritage elements of the historic downtown Winnipeg Hudson’s Bay Company building.
Held in trust by The Winnipeg Foundation, the capital invested in the Bay Building Fund will help preserve one of Winnipeg’s most cherished landmarks. The interest generated on the capital will be used to support Manitoba’s broader heritage sector.
Enhancing Capacity of Manitoba Public Libraries
Budget 2021 invested an additional $769,000 in rural and northern public libraries.
- $600,000 to be distributed to rural public libraries based on a per capita funding formula
- $100,000 toward sector development to support the long-term stability and sustainability of the sector
- $69,000 to ensure all Manitoba library systems have access to resources and services through the Centre for Equitable Library Access, a non-profit that offers library content for people with print disabilities
Manitoba’s investments in public libraries will contribute to their ability to provide high-quality services and programs to enhance the well-being of Manitobans in all regions of the province.
Investing in Our Communities
Investing in Public Safety
The major social and economic strain of the COVID-19 pandemic combined with Manitoba’s high crime rates is a significant concern for citizens and the province. Safe communities encourage people and businesses to stay and invest in the province, adding to economic well-being and stability.
Public safety plays a crucial role in this by improving the lives and well-being of those affected by crime, by keeping Manitobans safe in their communities and by building public confidence in a justice system that is responsive to the needs of Manitobans.
To enhance the policing and public safety environment in Manitoba, the Manitoba government is investing resources in 2022/23 for the following initiatives:
Manitoba is committed to working with First Nations communities, leaders, and organizations to expand the delivery of effective and culturally sensitive policing to all First Nations communities.
Manitoba invests in Budget 2022:
Continuing the implementation of the Police Services Act review The independent review of Manitoba’s Police Services Act examined the extent to which the act supports the professional, transparent and effective delivery of policing, and includes 70 recommendations. The department of justice established an implementation team that has been working directly with Indigenous organizations including the Assembly of Manitoba Chiefs (AMC), Manitoba Keewatinowi Okimakanak (MKO), the Southern Chiefs Organization (SCO) and the Manitoba Metis Federation and other targeted stakeholders to inform amendments to the legislation. On November 29, 2021, the Manitoba government introduced amendments to the Police Services Act that would strengthen the Independent Investigations Unit (IIU), address gaps in current legislation, address concerns raised by stakeholders, enhance relationships between the IIU and affected communities, and support greater responsiveness and accountability in policing across the province. On March 17, 2022, The Manitoba government introduced amendments to the Police Services Act that will enhance police work, sharing of police intelligence, establish provincial policing standards and a standard code of conduct for all police services across Manitoba. The bill will also extend the filing time for complaints under the Law Enforcement Review Act bringing it more in line with other provincial jurisdictions.
|
MCIC Funding |
2020-2021 |
2021-2022 |
2022-2023 |
Total Three- Year Funding |
|
Thousands of Dollars |
||||
|
PPSS |
$550 |
$550 |
$550 |
$1,650 |
|
GGVAF |
$716 |
$692 |
$838 |
$2,246 |
|
Total |
$1,266 |
$1,242 |
$1,388 |
$3,896 |
Continuing funding of $1 million for the expansion of community mobilization in 12 communities across Manitoba Community mobilization initiatives bring together law enforcement, social services, education and health care resources to provide at-risk Manitobans the support they need in the community. These coordinated efforts improve outcomes in education, employment, housing and family well-being. In addition, community mobilization efforts reduce contact with the justice system by addressing the root causes that led to the involvement. A Social Return on Investment study of a Manitoba community mobilization project showed that for every $1.00 invested, there is a $5.01 return on investment. Investments in community mobilization reflect best practice demonstrated through shared measurement, reporting, and evaluation. In 2020/21, outcomes from five community mobilization initiatives throughout Manitoba resulted in:
- 60 per cent decrease in calls to police under the Mental Health Act (youth clients)
- 62 per cent decrease in number of charges ( adult clients)
- 59 per cent decrease in the number of calls to police (adult clients)
Continuing to invest in the safety and well-being of citizens of Thompson – The Manitoba government continues to invest in safety and well-being initiatives for Thompson including building and operating a sobering centre to reduce its public intoxication calls, renovations for Thompson’s courthouse, re-establishment of StreetReach North in Thompson, and creating a community safety and well-being plan. From June 2020 to August 2021, StreetReach North helped return 473 children and youth to their placements or places of safety, and made 2,458 relationship-building contacts with youth.
Protecting Our Environment
Protecting Manitoba’s Climate and Environment
As the economy grows, the Manitoba government also knows it is imperative to address climate change and protect and restore the environment.Climate change is real and Manitobans are seeing its effects across the province as well as nationally and globally. The Manitoba government is making significant strides in protecting the natural environment and addressing the impacts of a changing climate. Manitoba continues to work on building capacity and moving forward with climate adaptation planning and investments in order to ensure a resilient future, including work to improve resilience in floods, drought and extreme events that affect communities, economy and environment. This includes the development of a comprehensive provincial water management strategy to conserve wetlands, enhance resiliency, improve surface water quality, manage nutrients, protect biodiversity and sustain economic development.
Manitobans are fortunate to have access to beautiful parks and trails to experience the environment, and the government continues to make strategic investments in infrastructure, trails and park visitor experience so outdoors can be enjoyed. The Manitoba government will continue working with stakeholders, Indigenous organizations and communities, and Manitobans to identify ways to enhance these amenities.
Investments in monitoring and remediation of orphaned and abandoned mines will help to protect the environment and communities from contamination, while innovation will reform how Manitoba manages waste and recycling to divert more waste from landfills. Environmental licensing will continue to support sustainable economic development while advancing reconciliation with Indigenous communities and guiding investment decisions.
Manitoba’s Climate and Green Plan
Manitoba’s Climate and Green Plan establishes clear objectives for reducing greenhouse gases in a way that is responsive to the unique nature of the province’s economy and emissions profile, promotes pathways for low-carbon growth, and harnesses the strengths as a leader in renewable energy. Manitoba’s November 2022 speech from the throne emphasized government`s commitment to working with the federal government on a national approach based on co-operation and consultation, and contributing to help Canada meet its international obligations reaffirmed at the United Nations climate change conference in Glasgow, Scotland.
Key actions undertaken to support Manitoba’s commitment to reduce emissions and contribute to ongoing national efforts to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 include:
- phase-down of Manitoba Hydro’s last coal-fired electricity generating unit and ceasing operations at Manitoba Hydro’s Selkirk Natural gas thermal generating facility
- ongoing delivery of Manitoba’s Efficient Trucking program, estimated cumulative emissions reductions associated with the program over the period spanning 2020 to 2030 are 85 ktCO2e in Manitoba and 244 ktCO2e in Canada
- scheduled increases to provincial biofuels mandate requirements for ethanol and biodiesel are projected to account for 10 per cent of Manitoba’s one megatonne greenhouse gas (GHG) goal for the first Carbon Savings Account period
- delivery of energy efficiency programs through Efficiency Manitoba. The new Crown agency is expected to reduce emissions in the province by an estimated 135 ktCO2e by 2023. Efficiency Manitoba is leveraging $32.3 million from Canada’s Low Carbon Economy Leadership Fund
Implementing Canada’s Updated Carbon Pricing Benchmark
Carbon Pricing in Manitoba
Manitoba is committed to working collaboratively with Canada and is developing a new approach to implementing Canada’s updated carbon pricing benchmark announced in December 2021. Manitoba recognizes the importance of doing its share to address climate change and contribute to Canada’s commitments under the Paris Accord and reaffirmed in Glasgow.
Manitoba is committed to working collaboratively with Canada to assess carbon-pricing options that achieve desired outcomes including:
- accessing and using carbon tax revenues in a manner that is tailored to aligned with Manitoba’s economy and tailored to provincial priorities
- achieving cost-effective GHG emissions across the economy
- minimizing administrative burden and red tape, and
- aligning with updated federal benchmark stringency requirements
Green Investments
Renewable Energy
Manitoba’s clean energy exports offset global emissions by approximately seven MtCO2e annually, representing roughly one-third of total provincial emissions. These exports were enabled by the 500-kilovolt Manitoba-Minnesota Transmission Project to transmit surplus hydroelectricity to the United States that came on line June 1, 2020. In 2020, Manitoba Hydro and SaskPower signed a power purchase agreement to export an additional 215 megawatts (MW) of hydroelectric capacity added to the SaskPower grid in 2022. The agreement will bring Manitoba Hydro’s total exports to SaskPower up to 315 MW. On March 29, 2021, the Birtle Transmission Project powered began delivering renewable hydropower from Manitoba to Saskatchewan.
GROW and Conservation Trusts
The Growing Outcomes in Watersheds (GROW) and Conservation Trusts launched in 2019 continue to support conservation and restoration of Manitoba wetlands, riparian and upland areas to support wildlife, water quality, groundwater recharge and carbon sinks.
As of March 31, 2022, a total of $12.464 million has been committed from Trust revenues to grantees for projects in Manitoba. Full results of the projects supported by investments from these trusts are not yet available because many projects are multi-year, but as of March 31, 2022, a total of 45 earlier projects have been completed and reported the following outcomes:
- 4,950 hectares of wetlands restored, enhanced, or conserved
- 4,750 acres of riparian areas restored, enhanced or conserved
- 38,200 acres of grassland and other perennial cover restored, enhanced, or conserved
- 250 surface acres of new water storage projects
- 4,000 acres of cover crop plantings
- 67 kilometres of shelterbelts planted or enhanced
Developing a Long-term Energy Strategy for Manitoba
Conservation and Climate Fund
Since its launch in 2019, the Conservation and Climate Fund continues to support eligible green initiatives that support key priorities of the Made-in-Manitoba Climate and Green Plan . The Conservation and Climate Fund increased by $400,000 to $1 million in 2021/22 and is increasing to $1.5 million in 2022/23. Grant recipients have included include incorporated non-profit organizations, academic and educational institutions, Manitoba municipalities and Northern Affairs communities, Indigenous communities, and businesses.
Manitoba’s new long-term energy strategy will articulate a modern vision for energy that will guide the use of provincial energy resources and technologies as a way to combat climate change, stimulate economic development, promote innovation and reduce the use of fossil fuels.
Driving Innovation: Green Outcomes Project
Manitoba Environment, Climate, Parks and Recreation has an outcomes-funded project underway to drive innovation and implement solutions to divert organic waste, promote green jobs and reduce greenhouse-gas emissions while sharing risk with the private sector. A local waste-to-energy company was selected as the service provider for the initiative through a competitive screening process.
The service provider will receive a $500,000 base payment for project initiation with its performance monitored through a project board governance structure. Manitoba will pay up to $500,000 for successful achievement of outcomes verified by a third-party evaluator.
The project will support innovation particularly in institutional, commercial and industrial sectors.
Waste Reduction and Recycling Support
A $10-per-tonne Waste Reduction and Recycling Support (WRARS) levy is applied to all waste disposed at Manitoba’s landfills. The WRARS levy generates approximately $8.7 million annual revenue and was created to discourage the disposal of waste in landfills, and generate funds to support waste reduction and diversion initiatives. Eighty per cent of the revenue is rebated to municipalities to promote recycling and the remaining 20 per cent is used to support strategic waste diversion initiatives including organic waste management, residential hazardous waste management and support for recycling organizations.
WRARS financial incentives support residential recycling programs, which represent a significant expense for municipalities and northern communities. They also support diversion of organic waste, which is key to achieving provincial waste diversion and GHG emissions targets. WRARS support for managing hazardous waste ensures consistent and safe disposal options are available which protects the environment, human health and safety.
The existing approach to recycling and waste diversion has been in place for over a decade. During this time, new products have entered the marketplace and new technologies have emerged.
In 2020/21, the department of environment, climate and parks engaged a consultant to conduct a review of Manitoba’s waste diversion and recycling framework. The resulting report presented policy actions and tools have been reviewed and developed into a plan for modernization.
The WRARS budget for 2022/23 will maintain consistent delivery of existing programs while the department develops next steps to enhance waste diversion and recycling in the province.
Orphaned and Abandoned Mines and Contaminated Sites Rehabilitation Programs
Orphaned and abandoned mines (OAM) and contaminated sites ($53 million as of December 2021) represent significant liabilities ($247 million as of December 2021) for the province in both monetary and environmental aspects . In an effort to reduce provincial liability, and to improve human health and environmental safety, Manitoba is making progress advancing remediation and rehabilitation activities at multiple abandoned mine and contaminated sites. Currently the OAM program has 11 contracts under administration with a total value of $145 million (2021/22). One of these OAM contracts is the $24.4 million subprogram that involves environmental monitoring and maintenance at six priority sites in addition to treatment of contaminated water at three of the sites.
Manitoba is making progress advancing remediation and rehabilitation activities at multiple abandoned mine and contaminated sites.
International Institute for Sustainability (IISD)
Manitoba’s five-year funding agreement with IISD runs until 2023/24 and provides up to $1.3 million annually to IISD. Funding is provided for activities that advance climate mitigation and adaptation research in Manitoba, and supports other strategic green priorities of the province. IISD also provides expert advice and support for policy development and program implementation to advance the core objectives of the Made-in-Manitoba Climate and Green Plan .
Low Carbon Government Office
The Low Carbon Government Office provides support to government departments and other government reporting entities to reduce GHG emissions and advance sustainable operations. The office continues to work across government to build capacity, promote data collection and reporting, and identify opportunities to reduce GHG emissions. In 2021, the office launched efforts to collect data from across government through RETScreen software in order to improve information on the environmental performance of government buildings.
The Low Carbon Government Office has the following focus areas:
- sustainable procurement of goods and services
- improving building design, construction and management
- zero-emission vehicles and reducing fuel consumption by vehicles and equipment
- innovative use and management of information and communication technologies
- improving waste reduction and waste management
Manitoba Climate Resilience Training (MCRT) Project
Manitoba continues to advance adaptation activities in partnership with Canada. The Manitoba Climate Resilience Training (MCRT) Project of the Manitoba government is funded through Canada’s BRACE program. The program is helping to build capacity and expertise of including engineers and planners, the business community in northern Manitoba, and Indigenous organizations and communities to address the risks associated with climate change.
New Green Investments 2022 – 2023
Conservation and Climate Fund
Building Capacity in Partnership with Municipalities
Manitoba will be supporting municipalities by providing information and training to help them access important funding opportunities available through the Federation of Canadian Municipalities (FCM) and new emerging funds. Over the next three years, this project will target key thematic areas to support municipal plans that will help municipalities access funding to undertake green initiatives within their communities. The project will provide municipalities with technical resources and tools to develop climate mitigation and resiliency plans, identify funding opportunities and support funding applications to a variety of external partners.
Greening Transportation
With almost 40 per cent of Manitoba’s emissions coming from transportation, Manitoba is developing new approaches to promoting green transportation, with the objective of achieving emissions reductions from this sector. The Expert Advisory Council (EAC) has provided advice and recommendations informing policy and programming regarding green transportation.
Actions under consideration for Manitoba are in the following areas:
- low-carbon and zero-emission transportation modes, technologies and practices
- coordinated land-use and transportation planning to promote the efficient movement of people, goods and materials
- enabling technologies and infrastructure
- innovation and economic development opportunities for clean technology in the transportation sector
Efficiency Manitoba
Innovation Fund
Efficiency Manitoba’s $2.1 million Innovation Fund launched in 2022 will see the development and advancement of innovative energy efficiency technologies and strategies in Manitoba.
Eligible projects can receive funding of up to 75 per cent of the project cost to a maximum of $250,000 with funding available under two streams: technology demonstration or market capacity.
Efficiency Manitoba’s objective through this program is developing successful projects into future Efficiency Manitoba initiatives.
The Indigenous Community Energy Efficiency Program also supports local economic development through energy efficiency by finding local labour solutions and contractors to complete the energy efficiency work. The application in-take period to apply for energy efficiency advocate funding occurs each fall from September to December.
Supporting Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Effective April 1, 2022, there will be $440,000 to fund 11 energy efficiency advocate positions in First Nation communities across Manitoba through Efficiency Manitoba’s Indigenous Community Energy Efficiency Program.
Extending Efficiency Manitoba’s three-year Efficiency Plan
Efficiency Manitoba commenced operations on April 1, 2020, which coincided with the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic in Manitoba. With a three-year plan for energy efficiency prepared pre-pandemic, customer participation in programs and therefore budget spend on programs during Efficiency Manitoba’s first two fiscal years of operations have been below levels projected in the 2020-23 Efficiency Plan. The organization has over 35 programs and offers in the market currently, and has been actively modifying programs, offering enhancements and increasing its communications and outreach. The full spend projected in the agency’s first three-year plan will not be realized due to persisting impacts of the pandemic.
On January 29, 2021, $32.3 million of Low Carbon Economy Leadership Funding (LCELF) to support Efficiency Manitoba’s natural gas efficiency programs was announced. Recognizing pandemic impacts on customer participation in programs, the Manitoba government is working with the federal government to maintain access to the full allocation of approved LCELF funding for Efficiency Manitoba. To enable this, a one-year extension to the current Efficiency Plan is required.
The Manitoba government has set an ambitious path toward a sustainable, prosperous future. As a leader in producing clean, renewable energy to power homes and businesses, vehicles and local industries, the province continues to find innovative ways to bend the emission curve downward. The benefits associated with growing a sustainable future will be felt everywhere – from farming communities to cities, Indigenous communities, and northern and remote regions of the province. Working together with all Manitobans and collaboratively with federal partners, implementing the ambitious Made-in-Manitoba Climate and Green Plan help us all move toward a greener and more resilient future.
Hydrologic Forecast: Spring Flood Outlook
Manitoba Transportation and Infrastructure’s Hydrologic Forecast Centre’s spring flood outlook reports a high risk of moderate flooding in the Red River Valley basin and minor flooding in other southern Manitoban basins due to the favourable conditions over the past weeks.While soil moisture in most Manitoba basins was below normal, precipitation since November 2021 has been above normal. The extent of flooding is highly dependent on the rate of snow melt and weather conditions, including spring rains. The Red River is expected to crest in mid-April. Ice cutting has been completed on the Red River to reduce the risk of ice jamming and Manitoba Transportation and Infrastructure expects to operate the Red River Floodway to reduce levels within the City of Winnipeg and expects to operate the Portage Diversion to control levels in the lower Assiniboine River. Manitoba’s major lakes are expected to be within their desirable operating ranges after spring runoff.


 Manitoba entered into a master services agreement with US Health Care Provider Sanford Health in Fargo, North Dakota in support of the Surgery and Diagnostics Recovery Program including authority to procure services for Neuro/Spine surgeries.
Manitoba entered into a master services agreement with US Health Care Provider Sanford Health in Fargo, North Dakota in support of the Surgery and Diagnostics Recovery Program including authority to procure services for Neuro/Spine surgeries.
